udev wrangling
Tuesday, June 25. 2013
Most Linux distros have udev. It has been around a while and is pretty much the way of handling physical devices in your box.
In The Old Age™ making a device to be something was very simple. /dev was in regular filesystem and could have permissions/symlinks/whatever set by admins. During modern era creating a symlink or setting permissions is bit more complex. The steps are:
- Identify the device
- Figure out the identifying attributes from udev
- Choose an operation / operations to be executed when the device is found
- This can be during boot or plug'n'play / USB
- Bring it all together in a configuration file readable by udev
An example:
External USB-drive/-stick can have pretty much any drive letter assigned into it by SCSI-subsystem during plugin. It can be /dev/sde today and /dev/sdf tomorrow. Trying to figure out the drive letter each time it is plugged in is both tedious and unnecessary. With (simple?) udev-wrangling you can have a /dev/myownusb to access it every time the drive is plugged in. Steps:
- Identify
- lsusb is your friend, from the output it is possible to determine that:
Bus 001 Device 007: ID 1941:8021 My C00l USB-drive - Today USB-bus 001 device 007 is the drive. What if you plug it into a different USB-port next time? We need to find identifying attribute/attributes to make configuring possible.
- If we assume that the drive is /dev/sdf this time, all the udev-attributes can be displayed with a:
udevadm info --query=all --name=/dev/sdf --attribute-walk - It will reveal a drive serial number in a format similar to:
ATTRS{serial}=="0000002CE09310500C1B" - The operation we'd like to be done when such a USB-device with a matching serial number is plugged into the computer is a symlink.
- The final step to get this configured would be to create a file into /etc/udev/rules.d/ with a suitable name.
- I chose my configuration to be /etc/udev/rules.d/99-mylocalrules.
- The file will contain a single line with identifying information and the operation. Example:
SUBSYSTEMS=="usb", ATTRS{serial}=="0000002CE09310500C1B", KERNEL=="sd?1", SYMLINK+="myownusb" - That literally reads: Whenever a new device is introduced into USB-subsystem with suitable serial number and having a partition, the 1st partition will be symlinked into udev with name "myownusb"
To get the rule into effect you need to run:
udevadm trigger
It is not necessary to unplug an already working drive. Just confirm that it worked:
ls -l /dev/myownusb
... or similar. Then just mount:
mount /dev/myownusb /mnt/myownusb
Another example:
I have a weather station connected into my Linux via USB-cable. There is no point of accessing it as a root, but out-of-the-box that's the only way to go. I need to chgrp the device after every boot for regular users to gain access into it.
With above process my identifying factor is the USB ID of the device and operation is to chgrp the device with a suitable group to allow access for those users belonging into the group. The rule is:
SUBSYSTEMS=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="1941", ATTR{idProduct}=="8021", GROUP="110"
Yet again the udev-rule reads: Whenever a new device is introduced into USB-subsystem with vendor ID of 0x1941 and product ID of 0x8021 the newly created udev-device will have a group with id 110. I prepared a group with groupadd and confirmed that it exists:
# getent group 110
WH-1080usb:*:110:itsme
After a udevadm trigger the result can be confirmed:
# ls -l /dev/bus/usb/001/007
crw-rw-r--. 1 root WH-1080usb 189, 6 Jun 19 10:07 /dev/bus/usb/001/007
The long(ish) path into the device comes from the lsusb output, it reads:
Bus 001 Device 007: ID 1941:8021 Dream Link WH1080 Weather Station
... and can be also translated as /dev/bus/usb/001/007. Simple, huh?
Figuring out Fedora 19 sysctl.conf
Monday, June 24. 2013
Fedora Linux guys replaced the ancient Initd with Systemd in Fedora 16. Bold move. I understand it had to be done. It speeds up booting and does a bunch of other things Initd can't or won't.
The classic story when introducing something new is that it has bugs. This particular time I struggled to get my Magic Sysrq key working on boot. Looks like Fedora people failed (at least) two times with it: Bug 760254 in Fedora 16 and Bug 924433 in Fedora 18 describe these shortcomings.
In short, the trouble with this new thing is that your changes won't take effect on boot. Most Linux admins never touch any of the sysctl(8)-settings and continue living successfully. Then there are rest of us, who tinker&tune their boxes to match their requirements. In Fedora Linux there is a directory of /etc/sysctl.d/ into a sysadmin may create a file with own settings to either override existing settings from /usr/lib/sysctl.d/ or set completely new values, which have only their kernel default set.
An example:
To set the Sysrq-key into "dangerous"-mode allowing all possible operations, the value of file /proc/sys/kernel/sysrq needs to be "1". It can be achieved with a file in /etc/sysctl.d/ containing following:
kernel.sysrq = 1
In Fedora the default value according to /usr/lib/sysctl.d/50-default.conf and manual inspection after boot is "16". So, the big trouble is to get the value of "1" stick. After a couple of reboots I realized that it is possible to test the functionality without booting the computer. As a root, simply run:
systemctl restart systemd-sysctl.service
... and watch what happens. The rather complex name of the service is something I couldn't figure out without Fedora discussion forums.
Anyway, after many many failures I concluded that my own settings need to be executed before the file 50-default.conf. To make things easier, systemd-sysctl.service first gathers a full list of files to be processed, then alphabetizes them and finally executes the settings in order. So I made my file to be /etc/sysctl.d/01-myownsettings.conf, which seemed to do the trick! There is a logic behind that, but it is just tricky to figure out.
Breaking php LDAP admin with PHP 5.5
Monday, June 17. 2013
Linux-distros are having a race for the most popular one. Part of the setup is to have the latest Linux kernel, and any other part of the software library a distro has. This effect yields into a "nice" effect where running the bleeding edge distros (Fedora, ArchLinux, Debian sid, etc.) every now and then something breaks.
The latest race is with PHP programming language which is nearing the 5.5.0 release. It has an RC3 version already out. Now the problem is that distro-guys start using the latest stuff, but PHP has incompatible changes in it. Plenty of things made with PHP 5.4 or 5.3 or ... won't run.
One of them is phpLDAPadmin. For some incomprehensible reason they are using stuff, which has been flagged as obsoleted years ago. So, it won't work. Luckily somebody at Debian made a fix. That makes my system's LDAP-admin working again. Hopefully somebody does the same with with all of the PEAR packages. ![]()
This is what you get when running alpha version of Fedora 19.
Windows 8 losing autoconfig IPv6-address after sleep
Sunday, June 16. 2013
Windows 7 and 8 IPv6-stack has a nice feature. Every now and then when waking up from sleep/hibernate there is no autoconfigured IPv6-address. It looks like this when checking for IPv6-address with netsh interface ipv6 show address:
Interface 12: WiFi
Addr Type DAD State Valid Life Pref. Life Address
--------- ----------- ---------- ---------- ------------------------
Other Preferred infinite infinite fe80::227:10ff:1234:5678%12
Note how there is only link-local address and no "proper" IPv6-address. On Windows 7 there is a fix. Just disable the Teredo-interface:
netsh interface teredo set state disabled
After that IPv6-autoconfiguration works much better. That doesn't do the trick for Windows 8, tough. I have no idea what would help. My only fix is to discard autoconfiguration and manually set an IPv6-address. This setting won't survive a reboot, so it will keep using autoconfig under normal conditions. But anyway, this is what I do to fix my laptop:
netsh interface ipv6 add address "WiFi" 2001:1234:5678:0:227:10ff:1234:5678
After this, netsh interface ipv6 show address will function properly:
Interface 12: WiFi
Addr Type DAD State Valid Life Pref. Life Address
--------- ----------- ---------- ---------- ------------------------
Manual Preferred infinite infinite 2001:1234:5678:0:227:10ff:1234:5678
Other Preferred infinite infinite fe80::227:10ff:1234:5678%12
If anybody knows how to fix this, please drop me a comment.
Linux distros moving all the important directories from / into /usr
Thursday, June 13. 2013
This is a cool move! At least Arch Linux and Fedora Linux have done this. A typical root directory listing will look like this:
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 May 30 23:17 bin -> usr/bin
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 May 30 23:17 lib -> usr/lib
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 9 May 30 23:17 lib64 -> usr/lib64
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 8 May 30 23:17 sbin -> usr/sbin
The /bin, /lib and /sbin have been in the root directory since first Unix was released in 1969. Any modern Linux distro won't have and won't need that many partitions than the legacy *nixes used to have. The reasoning is in this discussion thread.
Arch Linux guys have a pretty complex update process. The classic pacman -Syu won't do it for you this time.
Migrating into Samba 4 - part 2
Wednesday, June 12. 2013
On my previous post about Samba 4, I stumbled on printers.
I had a weird warning in my log:
../source3/param/loadparm.c:3121(lp_do_parameter)
Ignoring unknown parameter "printer admin"
printer admin = root
The fix to do is drop:
printer admin = root
from smb.conf. Instead it needs to be done run-time, like this:
smbpasswd -a root
net rpc rights grant root SePrintOperatorPrivilege
First a password is required for root-user. I have one in LDAP, but for some reason a local password is required too. After that permissions for printer administration are granted separately. That pretty much concentrates privilege handling out of any text-files.
The other issue was printer sharing to Windows. It had an easy fix. I deleted the existing printer from Windows and added it again. CUPS had renamed the printer and it was not available with the same name. A basic CUPS / Samba setup with cupsaddsmb does the trick.
Samba 4 ldaps:// server functionality
Monday, June 10. 2013
My Fedora 19 project continues... An attempt to get Samba working. They upgraded into version 4 and obviously my version 3 smb.conf had issues. See my article about getting Samba to use LDAP as userbase backend.
The obvious problem was, that it didn't work. ![]()
A log entry from the failue:
../source3/lib/smbldap.c:575(smbldap_start_tls)
Failed to issue the StartTLS instruction: Connect error
../source3/passdb/pdb_ldap.c:6531(pdb_ldapsam_init_common)
pdb_init_ldapsam: WARNING: Could not get domain info, nor add one to the domain. We cannot work reliably without it.
../source3/passdb/pdb_interface.c:177(make_pdb_method_name)
pdb backend ldapsam:ldap://my.server did not correctly init (error was NT_STATUS_CANT_ACCESS_DOMAIN_INFO)
I confirmed the existing settings:
passdb backend = ldapsam:ldap://my.server
ldap ssl = start tls
After a nice while of reading manual pages, an attempt to fix:
passdb backend = ldapsam:ldaps://my.server
ldap ssl = off
Yielded an improvement:
../source3/lib/smbldap.c:998(smbldap_connect_system)
failed to bind to server ldaps://my.server with dn="uid=root,ou=People,dc=my,dc=domain" Error: Can't contact LDAP server
TLS error -8179:Peer's Certificate issuer is not recognized.
../source3/passdb/pdb_ldap.c:6531(pdb_ldapsam_init_common)
pdb_init_ldapsam: WARNING: Could not get domain info, nor add one to the domain. We cannot work reliably without it.
../source3/passdb/pdb_interface.c:177(make_pdb_method_name)
pdb backend ldapsam:ldaps://my.server did not correctly init (error was NT_STATUS_CANT_ACCESS_DOMAIN_INFO)
This, however, was an easy fix. It was a simple SElinux issue:
To my amazement SElinux context does not change on a local unix-socket request. When Samba makes the request to get user information, the LDAPd certificate store needs to have proper SElinux type for the directory. OpenLDAP does not make such checks and works fully.semanage fcontext -a -t cert_t /etc/openldap/cacerts
restorecon -R -v /etc/openldap/cacerts
Also allowing requests to home directories too:
setsebool -P samba_enable_home_dirs 1
After all this, I was happy to get my Samba-shares working again. CUPS-printing does not. But I'll fix that on some day.
Proftpd setup on Fedora 19
Wednesday, June 5. 2013
I needed to transfer really big files (10+ GiB) between couple of servers. Since I was not in a hurry I decided to go with FTP. It performs very well when doing large file transfers, see File Transfer Protocol Performance Study for EUMETSAT Meteorological Data Distribution by students of Institute of Mathematics and Computer Science University of Latvia. Only Rsync could do better, and that is when the target is to transfer large number of files instead of small number of large files. In reality all the time it took me to set up the servers, I'd done transferring my files with any protocol. Really, any. But since I'm expecting to need this setup sometimes later, I went ahead with it.
Anyway, I chose to go with FTPd and since my Fedora 19 beta has one in built in repo, I went with Proftpd. Initial problems:
- It didn't work well (read: not even the simplest things you'd expect work) with IPv6, it took me 3 hours to figure this out.
Fix: I used IPv4 addresses instead of FQDNs. Everything started to work. - No anonymous FTP-access
- No anonymous FTP uploads
IPv6-issues
There is plenty of code like this:
pr_log_debug(DEBUG0,
"Unable to handle PASV for IPv6 address '%s', rejecting command",
pr_netaddr_get_ipstr(session.c->local_addr));
pr_response_add_err(R_501, "%s: %s", cmd->argv[0], strerror(xerrno));
So after I found about that, I just stopped using it.
Anonymous FTP-access
FTP isn't a secure protocol. It was once by 80s standards, but in 2013 Internet... well, no. So the best bet is not to use security at all! I'll place my security on the firewall, use anonymous logins and reduce attack surface by shutting the daemon down when I'm not expecting to need it.
Getting the anonymous FTP to work turned out to be semi-tricky. The daemon needs a -DANONYMOUS_FTP in the sysconfig. Also I needed to re-direct the anonymous FTP root directory into a dedicated partition instead of the out-of-the-box /var/ftp. My enforcing SElinux didn't like that. I had appropriate owner and group setup for the directories and files, but it turned out that my mount-directory had weird SElinux type and I decided to go with pretty generic var_t as directory type, then anonymous user was able to log in. The next thing was to make sure that actual FTP-stuff had SElinux type of public_content_t for access to directories and files to work. The final thing was to convince my SElinux to allow using of appropriate TCP-ports for FTPd:
setsebool -P ftpd_connect_all_unreserved=1
After that I had somewhat working anonymous FTP box.
Passive FTP from Windows
I didn't have any fancy software for testing the client side. All I had was a trustworthy ftp.exe on a Windows PowerShell. However, it operated only on active-FTP -mode, which in my opinion is completely obsoleted. It simply does not work at all with proper firewall setup, so I'd better using passive-FTP -mode. Well, then... how to lure the ancient FTP-client to use it? It wasn't obvious or easy, but luckily somebody else had the same problem and solved it. The solution is to use QUOTE-command for passing the FTP-protocol required PASV, like this:
Connected to 192.168.0.1.
220 FTP Server ready.
User (192.168.0.1:(none)): ftp
331 Anonymous login ok, send your complete email address as your password
Password:
230-
*** Welcome to this anonymous ftp server! ***
You are user 1 out of a maximum of 10 authorized anonymous logins.
The current time here is Wed Jun 05 15:25:31 2013.
If you experience any problems here, contact : root@localhost
230 Anonymous login ok, restrictions apply.
ftp> quote pasv
227 Entering Passive Mode (192,168,0,1,236,242).
That made passive mode work ok.
Allowing anonymous uploads
The last bit was trickiest, it was almost impossible to give Proftpd what it wanted. To my surprise it wasn't about directory permissions or SElinux. It was simply about configuration issue with <Limit> acting stupidly. Out-of-the-box, the config file apparently allows anonymous uploads. The problem is that it doesn't work. There is a line like this:
<Directory uploads/*>
But it should be like this:
<Directory /uploads>
I don't know why it must be like that, but after tinkering it for a very long time, that turned to be the key to my success. I also changed a <Limit READ> into <Limit LIST READ> to prevent getting directory listings from uploads-directory.
That concluded my setup. Just opening suitable IP-addressses and TCP-ports 20 and 21 made my files fly.
Mac OS X encrypted Timemachine USB-drive
Wednesday, May 22. 2013
I got a new iMac and wanted to use an USB-drive as Time Machine backup destination for it. When it comes to easily movable backup-drives, my policy is to encrypt them. If a drive is lost/stolen/misplaced, other people don't get to access my data.
When OS X sees an empty USB-drive, and there is no Time Machin already set up, it asks if you'd like to use the newly found drive as Time Machine backup destination, which is nice and user friendly. During Time Machine setup, there is a checkbox "Encrypt drive". I checked it, but whatwhatwhat?! It refused to work. Error message:
There was an error preparing the Time Machine backup disk "TimeMachine" and an additional explanation: The given file system is not supported on Core Storage.
Well... that's strange. I have no idea what a Core Storage is, or why an Apple formatted HFS+ partition would not be a valid (encrypted) backup destination.
Here is what I did. My drive was already formatted when I got it:
$ diskutil list disk3
/dev/disk3
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: GUID_partition_scheme *1.0 TB disk3
1: EFI 209.7 MB disk3s1
2: Microsoft Basic Data WD Backup 1000.0 GB disk3s2
There is a 1 TiB Western Digital drive with a NTFS-partition on it. So I had to delete the partition and create a better suitable one:
$ diskutil partitionDisk disk3 1 GPT HFS+ TimeMachine 1T
Started partitioning on disk3
Unmounting disk
Creating the partition map
Waiting for the disks to reappear
Formatting disk3s2 as Mac OS Extended with name TimeMachine
Initialized /dev/rdisk3s2 as a 931 GB HFS Plus volume
Mounting disk
Finished partitioning on disk3
/dev/disk3
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: GUID_partition_scheme *1.0 TB disk3
1: EFI 209.7 MB disk3s1
2: Apple_HFS TimeMachine 999.9 GB disk3s2
This is the partition setup that refuses to work.
After couple of hours of Googling I found the solution:
$ diskutil enableJournal disk3s2
Journaling has been enabled for volume TimeMachine on disk3s2
I seem to have misplaced the links already. Sorry. Anyway, the problem was that I didn't enable journaling on the partition. I can understand why that is a requirement for Time Machine. Having a journaled partition adds robustness to write operations. The real questions are:
- Why creating a HFS+ partition does not enable journaling automatically?
- On Linux creating EXT2 or EXT3 partition does not enable journaling automatically
- On Linux creating EXT4 journaling is enabled by default
- Why doesn't Time Machine state the reason?
- Saying that Core Storage is not supported is a bit vague!
Mac OS X terminal UTF-8 over SSH
Tuesday, May 21. 2013
Something weird happens in OS X Terminal locale settings. Whenever I open an SSH-connection to one of my Linux-boxes, they refuse to properly set up an UTF-8 locale.
The session goes something like this. Checking locale settings on OS X terminal:
$ locale
LANG=
LC_COLLATE="C"
LC_CTYPE="UTF-8"
LC_MESSAGES="C"
LC_MONETARY="C"
LC_NUMERIC="C"
LC_TIME="C"
LC_ALL=
Open SSH-connection and check locale settings on Linux end:
~> locale
locale: Cannot set LC_CTYPE to default locale: No such file or directory
locale: Cannot set LC_ALL to default locale: No such file or directory
LANG=en_US.UTF-8
LC_CTYPE=UTF-8
LC_NUMERIC="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_TIME="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_COLLATE="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_MONETARY="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_MESSAGES="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_PAPER="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_NAME="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_ADDRESS="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_TELEPHONE="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_MEASUREMENT="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_IDENTIFICATION="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_ALL=
Aow come on! Something went wrong.
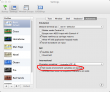
The fix on the OS X end is not to set the environment variables. In the Terminal settings, there is:
The setting Set locale environment variables on startup needs to be UNset. It is checked out-of-the-box. Then it yields:
$ locale
LANG=
LC_COLLATE="C"
LC_CTYPE="C"
LC_MESSAGES="C"
LC_MONETARY="C"
LC_NUMERIC="C"
LC_TIME="C"
LC_ALL=
The LC_CTYPE is not set. Over SSH-connection to Linux, it yields:
~> locale
LANG=en_US.UTF-8
LC_CTYPE="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_NUMERIC="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_TIME="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_COLLATE="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_MONETARY="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_MESSAGES="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_PAPER="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_NAME="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_ADDRESS="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_TELEPHONE="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_MEASUREMENT="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_IDENTIFICATION="en_US.UTF-8"
LC_ALL=
Now there are no error messages. The next thing to do is to try to find somebody responsible. Whose job it is to fix this.
Upcoming: Proper Hyper-V guest support for Linux
Thursday, May 16. 2013
Earlier I wrote about Linux 3.8 SCSI failing to operate under Hyper-V. Finally Microsoft has done something about it. After all, they are the biggest contributor for Linux kernel when it comes to running as a Hyper-V guest.
There is a patch-set fixing number of issues, for example: "Update the storage protocol to the win8 level." This means that they have seriously investigated the problems and fixed them. Also in the patch-set there are some new features, however, which are directed towards datacenters, not nerds like me running a Linux-box in the corner.
Great work from Mr. Srinivasan from Microsoft! Thank you for that.
Limiting Time Machine backup size on NAS
Monday, May 6. 2013
Earlier I wrote about getting a Linux-based NAS-box to host Apple Time Machine backups.
I was reviewing my settings on the Mac and realized the text in the Time Machine:
Well... I have lots of disk space there. Not all of it is can be taken by my Mac's backups, so ... Something needed to be done.
I mounted the AFP-share and confirmed the max size of my sparsebundle:
hdiutil imageinfo Mac\ mini.sparsebundle/
It said (unsurprisingly):
Size Information:
Total Bytes: 8855484092416
That is 8+ TiB!! Oh my! There is no way that I can afford to have that much of Apple backups. Luckily there is a way to reduce the size:
hdiutil resize -size 500g -shrinkonly Mac\ mini.sparsebundle/
Now checking the size will yield something reasonable (500 GiB):
Size Information:
Total Bytes: 537214885888
That is something, that I can easily accept.
The information came from:
- http://untoro.wordpress.com/2011/06/07/how-to-limit-space-used-by-time-machine/
- http://nikhilhaas.com/blog/limit-size-of-time-machine-backup-on-wd-my-book-live/
Also I did this to limit the size. I have no idea if it actually does anything.
defaults write /Library/Preferences/com.apple.TimeMachine MaxSize 405600
Perhaps somebody can comment this.
Linux 3.8 failing to operate as Hyper-V guest
Tuesday, April 16. 2013
Earlier I wrote about Hyper-V crashing with BSOD. The entire project was doomed from the beginning. After I managed get the Windows not to crash, all I managed to do is get the Linux installer to hang whenever it attempted to anything major on the hard drive. I configured Hyper-V to provide the hard drive from a .vhdx-file, so I initially suspected that old .vhd-file might help, but no, nothing helped. Any minor operations succeeded, but any sort of normal usage made the Linux to hang.
Symptoms include:
- Console message: "INFO: task jbd2/sda blocked for more than 120 seconds" and instruction to deactivate the warning with:
echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/hung_task_timeout_secs
Example: - Repeated "Sense Key" -messages in dmesg, example:
- No change in /sys/block/sda/stat:
- Kernel documentation about block-device stat says that columns 3 and 6 contain the number of sectors read and written.
- In my hung box, the values don't increase.
I was puzzled about this for a very long time. It took me several hours to bump into Linux-SCSI mailing list's discussion about the issue. There Mr. Olaf Hering describes an issue "storvsc loops with No Sense messages".
Luckily Mr. Hering realized what's going on and made a patch to fix the problem. Unfortunately the fix is not yet pushed into mainstream Linux kernel.
Since I was about to install ArchLinux, I took the trouble of compiling the necessary kernel module of hv_storvsc.ko into following kernel versions:
- 3.8.4, used in installation ISO-image:
- SHA-1 sum: 74d2a5de73a4c7d963b649eb34b171eba86a268c
- 3.8.6, the version that got installed when I got my install done:
- SHA-1 sum: 57a4216fc6749085820703d47cd87dcce47b1739
- 3.8.7, the version that it upgraded into when I did a system update:
- SHA-1 sum: 3f8757ab69c97a6389c7c83a8ef57f16e9caa85d
All of the packages are available for you to download at http://opensource.hqcodeshop.com/ArchLinux/2013.04.01/. Your only trick is to get them replaced into initial RAM-disk -image. I just replaced the original file at /usr/lib/modules and re-ran the mkinitrd-command.
Fedora 17: Ethernet interface lost
Monday, April 15. 2013
There was an update to my Fedora 17 Linux and among others, I got a new kernel. I didn't notice it at the time, but the reboot ate one of my Ethernet interfaces. There are two NICs on the motherboard, but on top of those, I have an Intel multi-port NIC. So in the end, there are more than your usual dose of ports.
Traffic to one particular LAN didn't function and I started to investigate:
# ifconfig -a
...
rename5: flags=4098<BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
ether 90:e2:ba:1d:33:f1 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
device memory 0xfe7e0000-fe800000
Well... I don't remember which one of my Ethernet-ports was rename5 after installation. Typically they are something like eth0, eth1 and so forth. Modern Linuxes tend to add more complexity with names like p2p2 or so, but I've never seen rename5-type naming.
From that I concluded that udev goofed up something. Fedora 17 does not create the /etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules-file which would solve my problem. Lot of Googling later, I found this page, it contains very useful Perl-script to dig enough system information and report it in udev-compatible format, in my case it yields:
# perl /root/bin/write_udev
...
# Added by 'write_udev' for detected device 'rename5'.
SUBSYSTEM=="net", ACTION=="add", DRIVERS=="?*", ATTR{address}=="90:e2:ba:1d:33:f1", NAME="rename5"
I created the persistent rule -file and added above into it. I just edited the NAME-part and renamed the interface properly.
Getting the rules to take effect was bit tricky. None of these worked:
udevadm trigger
udevadm control --reload-rules
udevadm trigger --attr-match=address='90:e2:ba:1d:33:f1'
udevadm trigger --sysname rename5
The trick was to get the full path with udevadm trigger --verbose --sysname rename5 -command and use the test-command with the full path:
udevadm test --action=add /sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:06.0/0000:02:00.1/net/rename5
Then I got my new rule to take effect immediately and my interface up and working.
Linux guest running on Hyper-V crashing with IRQL LESS OR NOT EQUAL
Wednesday, April 10. 2013
Since most modern Intel CPUs have VT-x in them and Windows 8 Pro has Hyper-V in it, I had to make use of the combo on my old laptop. It has a i5 mobile CPU which makes it on the less powerful end of CPUs. But the simple existence of a possibility of running a Linux on top of a Windows laptop makes me want to try it.
I added the Hyper-V feature into my Windows. I started the Hyper-V Management Console, added a virtual network switch and created a new virtual machine. It booted into Linux installer and the entire Windows crashed with a blue-screen-of-death. WTF?!
After a number of attempts with tweaking the Hyper-V settings, no avail. Every attempt to actually do anything reasonable in the guest system yielded a BSOD. Couple more futile attempts on command-line indicated that it had to have something to do with networking.
Next day I managed to Google into one discussion thread on Microsoft's social forums. There another unfortunate user is experiencing the same symptoms than me. Unlike his Windows 7, on my Windows 8 BSOD there isn't much of a stack trace or any usable information. But I had to try something, so I took an Ethernet-cable and plugged it into my laptop and reconfigured the Hyper-V virtual switch not to use the Intel Centrino 6200 WLAN, but a 1 Gbit/s Realtek port. That did the trick! Apparently some network drivers are not Hyper-V compatible. I don't know how to tell the difference between functioning or not functioning driver, but it is there.
There seems to be some sort of issue with hard drive, but that's an another story ...