Stop the insanity! There are TLDs longer than 4 characters
Wednesday, December 2. 2015
Software developers are stupid morons!
I have worked as one for couple of decades, so take my word for it. I know quite a few of them. Stupid morons, software developers and people who are both.
The reason for my rant is this JavaScript bugger:
var t = /^[A-Z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Z0-9.-]+\.[A-Z]{2,4}$/i;
It keeps popping up constantly. For people not familiar with regular expressions, that is a piece of code to match a valid e-mail address as specified by the one and only, original specification for ARPA Internet Text Messages, which we call e-mail today. As I keep insisting, software developers have major deficit both on writing proper code and testing their writtern code. For non-software developers: the reason that ill written line of code has spread around the internet like autumn flu, is that people just google for the regexp and copy/paste it into their product without thinking it for a second. It worked last time, right?
Here are the facts:
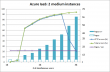
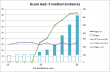
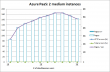
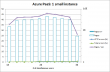
This is the list of IANA approved top-level-domains: http://data.iana.org/TLD/tlds-alpha-by-domain.txt in plain-text format. The list contains 1115 domains at the time of this vent. 570 of them are longer than 4 chars as limited by the above piece of crap. That results only 49% of valid TLDs being approved as valid ones. Anybody doing his/hers work only by 49% of success should be fired! Instantly.
Examples of valid TLDs:
As an example, the IANA list contains following domains: .cancerresearch, .xn--t60b56a, .international and .xn--vermgensberatung-pwb. The ones having lettersn XN, are internationalized domain names or IDNs. When decoded, .xn--c2br7g equals to नेट, .xn--t60b56a equals to 닷넷, both meaning .net in Hindi and Korean. Another ones are .xn--mgba3a3ejt for ارامكو, Saudi Aramco, the Saudi Arabian Oil Company and .xn--vermgensberatung-pwb for .vermögensberatung, German for financial advice. All of them are fully valid, but not being validated by the ancient piece of copy/paste mess everybody seems to be using.
Some of the weaker players:
The idiot-of-the-year -award doesn't go to http://www.moonfruit.com/ or http://tunnus.yle.fi/ who are strong competitors using that relic of a validator. The obvious winner is https://www.startssl.com/, who have a hard-coded list of 2827 domains and subdomains, having only 464 of the TLDs in the IANA-list. 651 of them missing, matching only 42% of the valid ones. Idiots!
If you are a software developer and reading this: It's time to shape up! Stop doing your job poorly.
Installing multi-user Ruby with RVM
Tuesday, November 24. 2015
I needed to run some Ruby-code in my Fedora-box, but the RPM-packaged version wasn't a decent or recent one. Since it is standard procedure and native to Ruby programming language to use Ruby version manager (or RVM), it also opens immense possibilities of running any existing Ruby version in same machine without the versions colliding with each other, this is definitely something that people need to know how to do.
There is plenty of good information about this in the net, for example How to Install Ruby 2.1.2 on CentOS & RHEL using RVM. However, the definite source is of course Installing RVM manual at RVM.io.
When it comes to multi-user installations, docs say "For server administrators - For an installation usable by all users on the system - This also used to be called the System-Wide Install. Using this type of installation without knowledge how umask works is a big security risk". RVM has a very simple filesystem permission -based security model, which will collapes if umask is not set correctly in multi-user mode. However, the worst-case scenarios include some gems have incorrect permissions set and only the user how installed it can un-install. Ultimate worst-case scenario is, that people not belogning to rvm-group can install and un-install modules. In a system-wide setup other people tampering with critical resources can be fatal, hence the obligatory warnings.
My case is much simpler, I need the same stuff for myself to develop with and for the system to run with. That's how I know I develop, test and run the same libraries. I wouldn't dream on sharing the stuff with other persons and calling that secure.
Back to setup of my RVM, current ruby version information:
$ ruby -v
ruby 2.0.0p353 (2013-11-22 revision 43784) [x86_64-linux]
To start the installation, a simple one-liner will do:
$ curl -sSL http://get.rvm.io | sudo bash -s stable -- --ignore-dotfiles
It will download the latest stable installer bash-script and immediately execute it with flag not to use user's own files. This is more suitable for machine-wide mode. The really important thing is to use sudo. Installation will fail to setup correctly, if doing it as root. Another security warning here: you will be trusting blindly on something you downloaded from the web. Hey! They call it open-source. ![]()
The installation will work only on Bourne shells. I'd recommend using Bash with all RVM-operations. The installer will say something like this:
Downloading https://github.com/rvm/rvm/archive/master.tar.gz
Creating group 'rvm'
Installing RVM to /usr/local/rvm/
Installation of RVM in /usr/local/rvm/ is almost complete:
First you need to add all users that will be using rvm to 'rvm' group,
and logout - login again, anyone using rvm will be operating with `umask u=rwx,g=rwx,o=rx`.
To start using RVM you need to run `source /etc/profile.d/rvm.sh`
in all your open shell windows, in rare cases you need to reopen all shell windows.
# Thank you for using RVM!
# We sincerely hope that RVM helps to make your life easier and more enjoyable!!!
#
# ~Wayne, Michal & team.
In case of problems: http://rvm.io/help and https://twitter.com/rvm_io
If your system didn't have an user group called rvm, it does now. As the instructions say, it's your task now to assign users to that group. You can do it like this:
$ getent group rvm
rvm:x:983:
Your group ID will change, of course. Add your user to this new group like this (I'm doing it as root, sudo will do the trick also):
# usermod -a -G rvm joeuser
# getent group rvm
rvm:x:983:joeuser
Yet again, the instructions above say, that this addition will NOT take effect until one of these happens:
- User logs in. If you're adding yourself, log out first.
newgrp-command is issued, newgrp(1) - Linux man page
RVM installer will add a file into /etc/profile.d/ to do some settings at login:
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 1203 Nov 23 19:39 /etc/profile.d/rvm.sh
If you need to have the settings in effect, all you need to do is source it:
$ source /etc/profile.d/rvm.sh
Anyway, now the rig is ready, we only need an installed Ruby version to get the ball rolling. To get an idea what's out there, get a list of all available Rubies there are:
$ rvm list known
# MRI Rubies
[ruby-]1.8.6[-p420]
[ruby-]1.8.7[-head] # security released on head
[ruby-]1.9.1[-p431]
[ruby-]1.9.2[-p330]
[ruby-]1.9.3[-p551]
[ruby-]2.0.0[-p647]
[ruby-]2.1[.7]
[ruby-]2.2[.3]
[ruby-]2.2-head
ruby-head
I'm urging to go for the install, but my first install attempt stalled on some missing libraries. There was a prompt asking for my password, but I chose not to enter my personal password to a script. So:
# yum install libyaml-devel readline-devel libffi-devel sqlite-devel
When those landed, let's go for an install:
$ rvm install ruby-2.1.7
The installer will output a lot, some of it is:
Searching for binary rubies, this might take some time.
No binary rubies available for: fedora/20/x86_64/ruby-2.1.7.
Continuing with compilation. Please read 'rvm help mount'
to get more information on binary rubies.
Checking requirements for fedora.
Requirements installation successful.
Installing Ruby from source to: /usr/local/rvm/rubies/ruby-2.1.7,
this may take a while depending on your cpu(s)...
ruby-2.1.7 - #downloading ruby-2.1.7,
this may take a while depending on your connection...
ruby-2.1.7 - #extracting ruby-2.1.7 to /usr/local/rvm/src/ruby-2.1.7....
ruby-2.1.7 - #configuring...
ruby-2.1.7 - #post-configuration..
ruby-2.1.7 - #compiling...
ruby-2.1.7 - #installing...
ruby-2.1.7 - #making binaries executable..
ruby-2.1.7 - #downloading rubygems-2.4.8
ruby-2.1.7 - #extracting rubygems-2.4.8....
ruby-2.1.7 - #removing old rubygems.........
ruby-2.1.7 - #installing rubygems-2.4.8...
ruby-2.1.7 - #gemset created /usr/local/rvm/gems/ruby-2.1.7@global
ruby-2.1.7 - #importing gemset /usr/local/rvm/gemsets/global.gems...
ruby-2.1.7 - #generating global wrappers........
ruby-2.1.7 - #gemset created /usr/local/rvm/gems/ruby-2.1.7
ruby-2.1.7 - #importing gemsetfile /usr/local/rvm/gemsets/default.gems
evaluated to empty gem list
ruby-2.1.7 - #generating default wrappers........
ruby-2.1.7 - #adjusting #shebangs for (gem irb erb ri rdoc testrb rake).
Install of ruby-2.1.7 - #complete
Ruby was built without documentation,
to build it run: rvm docs generate-ri
But ultimately, you're good to go:
$ ruby -v
ruby 2.1.7p400 (2015-08-18 revision 51632) [x86_64-linux]
To get back to my original task, I installed a gem:
$ gem install davclient
Fetching: davclient-0.0.8.gem (100%)
Successfully installed davclient-0.0.8
Parsing documentation for davclient-0.0.8
Installing ri documentation for davclient-0.0.8
Done installing documentation for davclient after 0 seconds
1 gem installed
That's it! Everything is ready.
PHP large file uploads
Thursday, March 20. 2014
Here I bumped into a really popular subject. My ownCloud had a really small upload limit of 32 MiB and I was aiming for the 1+ GiB range. The "cloud" is in a tiny box and is running a 32-bit Linux, so 2 GiB is the absolute maximum for a file that can pass trough Apache and PHP. The limits are documented in ownCloud Administrators Manual - Dealing with Big File Uploads.
Raising the file size limits is something I could do myself. Here is a reference for you: How to Upload Large Files in PHP. Its simply about finding the parameters for limits and setting them to a bigger value.
I created different size sample files and tested with them. I found out that there is a point after Apache started the upload, uploaded for a while and exited with a HTTP/500. In my case 600 MiB file passed ok, but 800 MiB file did not. I later found out, that it wasn't about the file sizes itself, but max input time. I had missed that one on my setup.
The max input time is a classic, for example a conversion with topic "PHP file upload affected or not by max_input_time?" discusses the issue in detail. The conclusion is that, the actual upload speed (or network bandwidth available) has nothing to do with the input processing, or maximum value of it. There is a PHP manual page of http://php.net/manual/en/features.file-upload.common-pitfalls.php and it clearly says:
max_input_time sets the maximum time, in seconds, the script is allowed to receive input;
this includes file uploads. For large or multiple files, or users on slower connections,
the default of 60 seconds may be exceeded.
But that simply is not true! In the another section of PHP manual the integer directive max_input_time is defined as:
This sets the maximum time in seconds a script is allowed to parse input data, like POST and GET. Timing begins at the moment PHP is invoked at the server and ends when execution begins.
When is PHP invoked? Let's say you're running Apache. You're actually uploading the file to Apache, which after receiving the file passes the control to a handler. PHP in this case. Surely the input processing does not start at the point where uploading starts.
Test setup
The upload is affected by following PHP configuration directives:
- file_uploads: The master switch. This one is rarely disabled as it makes any file upload processing impossible on PHP.
- Changeable: PHP_INI_SYSTEM
- upload_max_filesize: Max size of a single file.
- PHP_INI_PERDIR
- post_max_size: Max size of the entire upload batch. A HTTP POST can contain any number of files. In my test only one file is used.
- PHP_INI_PERDIR
- max_input_time: As discussed above, the time to parse the uploaded data and files. This would include populating $_FILES superglobal.
- PHP_INI_PERDIR
- max_execution_time: The time a script is allowed to run after its input has been parsed. This would include any processing of the file itself.
- PHP_INI_ALL
- memory_limit: The amount of memory a script is allowed to use during its execution. Has absolutely nothing to do with the size of the file uploaded, unless the script loads and processes the file.
- PHP_INI_ALL
- upload_tmp_dir: This is something I threw in based on testing. None of the articles ever mention this one. This defines the exact location where the uploaded file initially goes. If the PHP-script does not move the uploaded file out of this temporary location, the file will be deleted when script stops executing. Make sure you have enough space at this directory for large files!
- PHP_INI_SYSTEM
A PHP script cannot change all of the introduced configuration values. The changeable limits are defined as:
- PHP_INI_USER: Entry can be set in user scripts (like with ini_set())
- PHP_INI_PERDIR: Entry can be set in php.ini, .htaccess, httpd.conf
- PHP_INI_SYSTEM: Entry can be set in php.ini or httpd.conf
For testing purposes I chose the POST and upload max sizes to be 1 GiB (or 1024 MiB). To test the timeout values, I chose relatively small values of 2 seconds both for input parsing and script execution. Also to prove that memory limit does not limit the file upload, I chose the available memory for the script to be 1 MiB. The memory limit is not an issue, as my script does not touch the file, does not try to load or process it.
My test script carefully enforces the above limits just to make sure, that there is no configuration mistakes.
Sample files were generated out of randomness with a command:
dd if=/dev/urandom of=900M bs=1024 count=921600
A number of files of different size was used, but since the POST-limit was set to 1 GiB or 1073741824 bytes, it is impossible to upload a file of the same size. There is always some overhead in a HTTP POST-request. So, the maximum file size I succesfully used with these parameters was 900 MiB. Interestingy it was the 2 second input processing time which caused problems.
The sample code:
<?php
// Adapted by JaTu 2014 from code published in
// http://stackoverflow.com/questions/11387113/php-file-upload-affected-or-not-by-max-input-time
$iniValues = array(
'file_uploads' => '1', // PHP_INI_SYSTEM
'upload_max_filesize' => '1024M', // PHP_INI_PERDIR
'post_max_size' => '1024M', // PHP_INI_PERDIR
'max_input_time' => '2', // PHP_INI_PERDIR
'max_execution_time' => '2', // PHP_INI_ALL
'memory_limit' => '1M', // PHP_INI_ALL
);
$iniValuesToSet = array('max_execution_time', 'memory_limit');
$upload_max_filesize_inBytes = 1073741824; // 1 GiB
foreach ($iniValues as $variable => $value) {
$cur = ini_get($variable);
if ($cur !== $value) {
if (in_array($variable, $iniValuesToSet)) {
$prev = ini_set($variable, $value);
if ($prev === false) {
// Assume the previous value was not FALSE, but the set failed.
// None of those variables can reasonable have a boolean value of FALSE anyway.
die('Failed to ini_set() a value into variable ' . $variable);
}
} else {
die('Failed to ini_set() a value into variable ' . $variable . ' and make it stick.');
}
}
}
if (!empty($_FILES) && isset($_FILES['userfile'])) {
switch ($_FILES['userfile']["error"]) {
case UPLOAD_ERR_OK:
$status = 'There is no error, the file uploaded with success.';
break;
case UPLOAD_ERR_INI_SIZE:
$status = 'The uploaded file exceeds the upload_max_filesize directive in php.ini.';
break;
case UPLOAD_ERR_FORM_SIZE:
$status = 'The uploaded file exceeds the MAX_FILE_SIZE directive that was specified in the HTML form.' .
' Value is set to: ' . $_POST['MAX_FILE_SIZE'];
break;
case UPLOAD_ERR_PARTIAL:
$status = 'The uploaded file was only partially uploaded.';
break;
case UPLOAD_ERR_NO_FILE:
$status = 'No file was uploaded.';
break;
case UPLOAD_ERR_NO_TMP_DIR:
$status = 'Missing a temporary folder.';
break;
case UPLOAD_ERR_CANT_WRITE:
$status = 'Failed to write file to disk.';
break;
case UPLOAD_ERR_EXTENSION:
$status = 'A PHP extension stopped the file upload. PHP does not provide a way to ascertain which extension caused the file upload to stop; examining the list of loaded extensions with phpinfo() may help.';
break;
default:
$status = 'No idea. Huh?';
}
print "Status: {$status}<br/>\n";
print '<pre>';
var_dump($_FILES);
print '</pre>';
}
?>
<form enctype="multipart/form-data" method="POST">
<input type="hidden" name="MAX_FILE_SIZE" value="<?php print $upload_max_filesize_inBytes ?>" />
File: <input name="userfile" type="file" />
<input type="submit" value="Upload" />
</form>
Test 1: PHP 5.5.10 / Apache 2.4.7
This is a basic Fedora 19 box with standard packages installed. PHP reports Server API as Apache 2.0 Handler.
To get the required setup done I had a .htaccess-file with following contents:
php_value upload_max_filesize "1024M"
php_value post_max_size "1024M"
php_value max_input_time 2
I used time-command from bash-shell combined with a cURL-request like this:
curl --include --form userfile=@800M http://the.box/php/upload.php
Timing results would be:
real 0m7.595s
user 0m1.044s
sys 0m3.259s
That is 7.5 seconds wallclock time to upload a 800 MiB file. The time includes any transfer over my LAN and processing done on the other side. No failures were recorded for the 2 second time limits or memory limits.
Errors would include:
- PHP Warning: POST Content-Length of 1073742140 bytes exceeds the limit of 1073741824 bytes in Unknown on line 0
- When POST-limit was exceeded
- PHP Fatal error: Maximum execution time of 2 seconds exceeded in Unknown on line 0
- When input processing took too long time
Warning!
Apache paired with PHP was especially difficult on situations where a HTTP/500 would occur for any reason. The temporary file would NOT be cleaned up immediate after the PHP-script died. The cleaning would occur at the point where Apache worker process would be recycled. Sometimes my temp-drive ran out of disc space an I had to manually trigger an Apache service restart to free up the space. But if you're in server exploiting business and manage to find one that allows large file uploads, it is possible to cause a resource exhaustion for the disc space by simply uploading very large files repeatedly. When upload fails the space is not immediately freed.
Test 2: PHP 5.4.26 / Nginx 1.4.6
To confirm that this is not an Apache-thing or limited to latest version of PHP, I did a second run with a different setup. I took my trustworthy Nginx equipped with PHP-FPM running on a virtualized CentOS. This time I didn't use standard components and used only packages compiled and tailored for my own web server. PHP reports Server API as FPM/FastCGI.
My /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf had:
php_admin_value[upload_max_filesize] = "1024M"
php_admin_value[post_max_size] = "1024M"
php_admin_value[max_input_time] = "2"
php_admin_value[max_execution_time] = 2
php_admin_value[memory_limit] = 1M
PHP's own ini_set()-function was unable to set any of the values, including those it was allowed to change. I didn't investigate the reason for that and chose to declare all of the required settings in the worker definition.
To get large POSTs into Nginx, my /etc/nginx/nginx.conf had:
location ~ \.php$ {
client_max_body_size 1024M;
}
Timing results would be:
real 0m16.170s
user 0m1.060s
sys 0m2.854s
That is 16.1 seconds wallclock time to upload a 800 MiB file. The time includes any transfer over my LAN and processing done on the other side. No failures were recorded for the 2 second time limits or memory limits.
Errors would include:
- 413 Request Entity Too Large
- On the browser end
- *22 client intended to send too large body: 838861118 bytes
- On the Nginx error log
If max POST size was hit.
Conclusions
As found in the net max_input_time and max_execution_time have nothing to do with the network transfer. Both of those limits affect only server's processing after the bytes are transferred.
PHP bashing: fractal of bad design?
Wednesday, March 5. 2014
I was inspecting the already fallen Bitcoin exhange Mt. Gox's source code at PasteBin and found a nice discussion thread about it at Hacker News with the title of Alleged Mt.Gox code leaked on IRC node by Russian Hacker. To my great surprise, the Bitcoin exchange was written with PHP by Mark Karpeles (aka. MagicalTux), the CEO/owner of Mt. Gox. According to number of sources thinks he is some kind of PHP-deity. Based on his (alleged) work posted to Bitcoin, I'd say no.
Anyway, I got lost reading Mr. Alex Munroe's (aka. veekun) rant about PHP. It is so good stuff, I'll have to copy/paste his entire very long blog post here as-is just to make sure it is not lost in the digital world. To repeat: I did not write this. This does not reflect my opinions. It is just a comprehensive list of all the weird things that bug Mr. Munroe. All rights for this are his, not mine. And lot of thanks for gathering this huge list.
Here goes:
Preface
I’m cranky. I complain about a lot of things. There’s a lot in the world of technology I don’t like, and that’s really to be expected—programming is a hilariously young discipline, and none of us have the slightest clue what we’re doing. Combine with Sturgeon’s Law, and I have a lifetime’s worth of stuff to gripe about.
This is not the same. PHP is not merely awkward to use, or ill-suited for what I want, or suboptimal, or against my religion. I can tell you all manner of good things about languages I avoid, and all manner of bad things about languages I enjoy. Go on, ask! It makes for interesting conversation.
PHP is the lone exception. Virtually every feature in PHP is broken somehow. The language, the framework, the ecosystem, are all just bad. And I can’t even point out any single damning thing, because the damage is so systemic. Every time I try to compile a list of PHP gripes, I get stuck in this depth-first search discovering more and more appalling trivia. (Hence, fractal.)
PHP is an embarrassment, a blight upon my craft. It’s so broken, but so lauded by every empowered amateur who’s yet to learn anything else, as to be maddening. It has paltry few redeeming qualities and I would prefer to forget it exists at all.
But I’ve got to get this out of my system. So here goes, one last try.
An analogy
I just blurted this out to Mel to explain my frustration and she insisted that I reproduce it here.
I can’t even say what’s wrong with PHP, because— okay. Imagine you have uh, a toolbox. A set of tools. Looks okay, standard stuff in there.
You pull out a screwdriver, and you see it’s one of those weird tri-headed things. Okay, well, that’s not very useful to you, but you guess it comes in handy sometimes.
You pull out the hammer, but to your dismay, it has the claw part on both sides. Still serviceable though, I mean, you can hit nails with the middle of the head holding it sideways.
You pull out the pliers, but they don’t have those serrated surfaces; it’s flat and smooth. That’s less useful, but it still turns bolts well enough, so whatever.
And on you go. Everything in the box is kind of weird and quirky, but maybe not enough to make it completely worthless. And there’s no clear problem with the set as a whole; it still has all the tools.
Now imagine you meet millions of carpenters using this toolbox who tell you “well hey what’s the problem with these tools? They’re all I’ve ever used and they work fine!” And the carpenters show you the houses they’ve built, where every room is a pentagon and the roof is upside-down. And you knock on the front door and it just collapses inwards and they all yell at you for breaking their door.
That’s what’s wrong with PHP.
Stance
I assert that the following qualities are important for making a language productive and useful, and PHP violates them with wild abandon. If you can’t agree that these are crucial, well, I can’t imagine how we’ll ever agree on much.
- A language must be predictable. It’s a medium for expressing human ideas and having a computer execute them, so it’s critical that a human’s understanding of a program actually be correct.
- A language must be consistent. Similar things should look similar, different things different. Knowing part of the language should aid in learning and understanding the rest.
- A language must be concise. New languages exist to reduce the boilerplate inherent in old languages. (We could all write machine code.) A language must thus strive to avoid introducing new boilerplate of its own.
- A language must be reliable. Languages are tools for solving problems; they should minimize any new problems they introduce. Any “gotchas” are massive distractions.
- A language must be debuggable. When something goes wrong, the programmer has to fix it, and we need all the help we can get.
My position is thus:
- PHP is full of surprises:
mysql_real_escape_string,E_ALL - PHP is inconsistent:
strpos,str_rot13 - PHP requires boilerplate: error-checking around C API calls,
=== - PHP is flaky:
==,foreach ($foo as &$bar) - PHP is opaque: no stack traces by default or for fatals, complex error reporting
I can’t provide a paragraph of commentary for every single issue explaining why it falls into these categories, or this would be endless. I trust the reader to, like, think.
Don’t comment with these things
I’ve been in PHP arguments a lot. I hear a lot of very generic counter-arguments that are really only designed to halt the conversation immediately. Don’t pull these on me, please. ![]()
- Do not tell me that “good developers can write good code in any language”, or bad developers blah blah. That doesn’t mean anything. A good carpenter can drive in a nail with either a rock or a hammer, but how many carpenters do you see bashing stuff with rocks? Part of what makes a good developer is the ability to choose the tools that work best.
- Do not tell me that it’s the developer’s responsibility to memorize a thousand strange exceptions and surprising behaviors. Yes, this is necessary in any system, because computers suck. That doesn’t mean there’s no upper limit for how much zaniness is acceptable in a system. PHP is nothing but exceptions, and it is not okay when wrestling the language takes more effort than actually writing your program. My tools should not create net positive work for me to do.
- Do not tell me “that’s how the C API works”. What on Earth is the point of using a high-level language if all it provides are some string helpers and a ton of verbatim C wrappers? Just write C! Here, there’s even a CGI library for it.
- Do not tell me “that’s what you get for doing weird things”. If two features exist, someday, someone will find a reason to use them together. And again, this isn’t C; there’s no spec, there’s no need for “undefined behavior”.
- Do not tell me that Facebook and Wikipedia are built in PHP. I’m aware! They could also be written in Brainfuck, but as long as there are smart enough people wrangling the things, they can overcome problems with the platform. For all we know, development time could be halved or doubled if these products were written in some other language; this data point alone means nothing.
- Ideally, don’t tell me anything! This is my one big shot; if this list doesn’t hurt your opinion of PHP, nothing ever will, so stop arguing with some dude on the Internet and go make a cool website in record time to prove me wrong

Side observation: I loooove Python. I will also happily talk your ear off complaining about it, if you really want me to. I don’t claim it’s perfect; I’ve just weighed its benefits against its problems and concluded it’s the best fit for things I want to do.
And I have never met a PHP developer who can do the same with PHP. But I’ve bumped into plenty who are quick to apologize for anything and everything PHP does. That mindset is terrifying.
PHP
Core language
CPAN has been called the “standard library of Perl”. That doesn’t say much about Perl’s standard library, but it makes the point that a solid core can build great things.
Philosophy
- PHP was originally designed explicitly for non-programmers (and, reading between the lines, non-programs); it has not well escaped its roots. A choice quote from the PHP 2.0 documentation, regarding
+and friends doing type conversion:Once you start having separate operators for each type you start making the language much more complex. ie. you can’t use ‘==’ for stings [sic], you now would use ‘eq’. I don’t see the point, especially for something like PHP where most of the scripts will be rather simple and in most cases written by non-programmers who want a language with a basic logical syntax that doesn’t have too high a learning curve.
- PHP is built to keep chugging along at all costs. When faced with either doing something nonsensical or aborting with an error, it will do something nonsensical. Anything is better than nothing.
- There’s no clear design philosophy. Early PHP was inspired by Perl; the huge stdlib with “out” params is from C; the OO parts are designed like C++ and Java.
- PHP takes vast amounts of inspiration from other languages, yet still manages to be incomprehensible to anyone who knows those languages.
(int)looks like C, butintdoesn’t exist. Namespaces use\. The new array syntax results in[key => value], unique among every language with hash literals. - Weak typing (i.e., silent automatic conversion between strings/numbers/et al) is so complex that whatever minor programmer effort is saved is by no means worth it.
- Little new functionality is implemented as new syntax; most of it is done with functions or things that look like functions. Except for class support, which deserved a slew of new operators and keywords.
- Some of the problems listed on this page do have first-party solutions—if you’re willing to pay Zend for fixes to their open-source programming language.
- There is a whole lot of action at a distance. Consider this code, taken from the PHP docs somewhere.
What will it do?@fopen('http://example.com/not-existing-file', 'r');- If PHP was compiled with
--disable-url-fopen-wrapper, it won’t work. (Docs don’t say what “won’t work” means; returns null, throws exception?) Note that this flag was removed in PHP 5.2.5. - If
allow_url_fopenis disabled in php.ini, this still won’t work. (How? No idea.) - Because of the
@, the warning about the non-existent file won’t be printed. - But it will be printed if
scream.enabledis set in php.ini. - Or if
scream.enabledis set manually withini_set. - But not if the right
error_reportinglevel isn’t set. - If it is printed, exactly where it goes depends on
display_errors, again in php.ini. Orini_set.
- If PHP was compiled with
- The language is full of global and implicit state.
mbstringuses a global character set.func_get_argand friends look like regular functions, but operate on the currently-executing function. Error/exception handling have global defaults.register_tick_functionsets a global function to run every tick—what?! - There is no threading support whatsoever. (Not surprising, given the above.) Combined with the lack of built-in
fork(mentioned below), this makes parallel programming extremely difficult. - Parts of PHP are practically designed to produce buggy code.
json_decodereturns null for invalid input, even though null is also a perfectly valid object for JSON to decode to—this function is completely unreliable unless you also calljson_last_errorevery time you use it.array_search,strpos, and similar functions return0if they find the needle at position zero, but false if they don’t find it at all.
Let me expand on that last part a bit.
In C, functions like
strposreturn-1if the item isn’t found. If you don’t check for that case and try to use that as an index, you’ll hit junk memory and your program will blow up. (Probably. It’s C. Who the fuck knows. I’m sure there are tools for this, at least.)In, say, Python, the equivalent
.indexmethods will raise an exception if the item isn’t found. If you don’t check for that case, your program will blow up.In PHP, these functions return false. If you use
FALSEas an index, or do much of anything with it except compare with===, PHP will silently convert it to0for you. Your program will not blow up; it will, instead, do the wrong thing with no warning, unless you remember to include the right boilerplate around every place you usestrposand certain other functions.This is bad! Programming languages are tools; they’re supposed to work with me. Here, PHP has actively created a subtle trap for me to fall into, and I have to be vigilant even with such mundane things as string operations and equality comparison. PHP is a minefield.
I have heard a great many stories about the PHP interpreter and its developers from a great many places. These are from people who have worked on the PHP core, debugged PHP core, interacted with core developers. Not a single tale has been a compliment.
So I have to fit this in here, because it bears repeating: PHP is a community of amateurs. Very few people designing it, working on it, or writing code in it seem to know what they’re doing. (Oh, dear reader, you are of course a rare exception!) Those who do grow a clue tend to drift away to other platforms, reducing the average competence of the whole. This, right here, is the biggest problem with PHP: it is absolutely the blind leading the blind.
Okay, back to facts.
Operators
==is useless.- It’s not transitive.
"foo" == TRUE, and"foo" == 0… but, of course,TRUE != 0. ==converts to numbers when possible (123 == "123foo"… although"123" != "123foo"), which means it converts to floats when possible. So large hex strings (like, say, password hashes) may occasionally compare true when they’re not. Even JavaScript doesn’t do this.- For the same reason,
"6" == " 6","4.2" == "4.20", and"133" == "0133". But note that133 != 0133, because0133is octal. But"0x10" == "16"and"1e3" == "1000"! ===compares values and type… except with objects, where===is only true if both operands are actually the same object! For objects,==compares both value (of every attribute) and type, which is what===does for every other type. What.
- It’s not transitive.
- Comparison isn’t much better.
- It’s not even consistent:
NULL < -1, andNULL == 0. Sorting is thus nondeterministic; it depends on the order in which the sort algorithm happens to compare elements. - The comparison operators try to sort arrays, two different ways: first by length, then by elements. If they have the same number of elements but different sets of keys, though, they are uncomparable.
- Objects compare as greater than anything else… except other objects, which they are neither less than nor greater than.
- For a more type-safe
==, we have===. For a more type-safe<, we have… nothing."123" < "0124", always, no matter what you do. Casting doesn’t help, either.
- It’s not even consistent:
- Despite the craziness above, and the explicit rejection of Perl’s pairs of string and numeric operators, PHP does not overload
+.+is always addition, and.is always concatenation. - The
[]indexing operator can also be spelled{}. []can be used on any variable, not just strings and arrays. It returns null and issues no warning.[]cannot slice; it only retrieves individual elements.foo()[0]is a syntax error. (Fixed in PHP 5.4.)-
Unlike (literally!) every other language with a similar operator,
?:is left associative. So this:$arg = 'T'; $vehicle = ( ( $arg == 'B' ) ? 'bus' : ( $arg == 'A' ) ? 'airplane' : ( $arg == 'T' ) ? 'train' : ( $arg == 'C' ) ? 'car' : ( $arg == 'H' ) ? 'horse' : 'feet' ); echo $vehicle;prints
horse.
Variables
- There is no way to declare a variable. Variables that don’t exist are created with a null value when first used.
- Global variables need a
globaldeclaration before they can be used. This is a natural consequence of the above, so it would be perfectly reasonable, except that globals can’t even be read without an explicit declaration—PHP will quietly create a local with the same name, instead. I’m not aware of another language with similar scoping issues. - There are no references. What PHP calls references are really aliases; there’s nothing that’s a step back, like Perl’s references, and there’s no pass-by-object identity like in Python.
- “Referenceness” infects a variable unlike anything else in the language. PHP is dynamically-typed, so variables generally have no type… except references, which adorn function definitions, variable syntax, and assignment. Once a variable is made a reference (which can happen anywhere), it’s stuck as a reference. There’s no obvious way to detect this and un-referencing requires nuking the variable entirely.
- Okay, I lied. There are “SPL types” which also infect variables:
$x = new SplBool(true); $x = "foo";will fail. This is like static typing, you see. - A reference can be taken to a key that doesn’t exist within an undefined variable (which becomes an array). Using a non-existent array normally issues a notice, but this does not.
- Constants are defined by a function call taking a string; before that, they don’t exist. (This may actually be a copy of Perl’s
use constantbehavior.) - Variable names are case-sensitive. Function and class names are not. This includes method names, which makes camelCase a strange choice for naming.
Constructs
array()and a few dozen similar constructs are not functions.arrayon its own means nothing,$func = "array"; $func();doesn’t work.- Array unpacking can be done with the
list($a, $b) = ...operation.list()is function-like syntax just likearray. I don’t know why this wasn’t given real dedicated syntax, or why the name is so obviously confusing. (int)is obviously designed to look like C, but it’s a single token; there’s nothing calledintin the language. Try it: not only doesvar_dump(int)not work, it throws a parse error because the argument looks like the cast operator.(integer)is a synonym for(int). There’s also(bool)/(boolean)and(float)/(double)/(real).- There’s an
(array)operator for casting to array and an(object)for casting to object. That sounds nuts, but there’s almost a use: you can use(array)to have a function argument that’s either a single item or a list, and treat it identically. Except you can’t do that reliably, because if someone passes a single object, casting it to an array will actually produce an array containing that object’s attributes. (Casting to object performs the reverse operation.) include()and friends are basically C’s#include: they dump another source file into yours. There is no module system, even for PHP code.- There’s no such thing as a nested or locally-scoped function or class. They’re only global. Including a file dumps its variables into the current function’s scope (and gives the file access to your variables), but dumps functions and classes into global scope.
- Appending to an array is done with
$foo[] = $bar. echois a statement-y kind of thing, not a function.empty($var)is so extremely not-a-function that anything but a variable, e.g.empty($var || $var2), is a parse error. Why on Earth does the parser need to know aboutempty? (Fixed in 5.5.)- There’s redundant syntax for blocks:
if (...): ... endif;, etc.
Error handling
- PHP’s one unique operator is
@(actually borrowed from DOS), which silences errors. - PHP errors don’t provide stack traces. You have to install a handler to generate them. (But you can’t for fatal errors—see below.)
- PHP parse errors generally just spew the parse state and nothing more, making a forgotten quote terrible to debug.
- PHP’s parser refers to e.g.
::internally asT_PAAMAYIM_NEKUDOTAYIM, and the<<operator asT_SL. I say “internally”, but as above, this is what’s shown to the programmer when::or<<appears in the wrong place. - Most error handling is in the form of printing a line to a server log nobody reads and carrying on.
E_STRICTis a thing, but it doesn’t seem to actually prevent much and there’s no documentation on what it actually does.E_ALLincludes all error categories—exceptE_STRICT. (Fixed in 5.4.)-
Weirdly inconsistent about what’s allowed and what isn’t. I don’t know how
E_STRICTapplies here, but these things are okay:- Trying to access a non-existent object property, i.e.,
$foo->x. (warning) - Using a variable as a function name, or variable name, or class name. (silent)
- Trying to use an undefined constant. (notice)
- Trying to access a property of something that isn’t an object. (notice)
- Trying to use a variable name that doesn’t exist. (notice)
2 < "foo"(silent)foreach (2 as $foo);(warning)
And these things are not:
- Trying to access a non-existent class constant, i.e.,
$foo::x. (fatal error) - Using a constant string as a function name, or variable name, or class name. (parse error)
- Trying to call an undefined function. (fatal error)
- Leaving off a semicolon on the last statement in a block or file. (parse error)
- Using
listand various other quasi-builtins as method names. (parse error) - Subscripting the return value of a function, i.e.,
foo()[0]. (parse error; okay in 5.4, see above)
There are a good few examples of other weird parse errors elsewhere in this list.
- Trying to access a non-existent object property, i.e.,
- The
__toStringmethod can’t throw exceptions. If you try, PHP will… er, throw an exception. (Actually a fatal error, which would be passable, except…) - PHP errors and PHP exceptions are completely different beasts. They don’t seem to interact at all.
- PHP errors (internal ones, and calls to
trigger_error) cannot be caught withtry/catch. - Likewise, exceptions do not trigger error handlers installed by
set_error_handler. - Instead, there’s a separate
set_exception_handlerwhich handles uncaught exceptions, because wrapping your program’s entry point in atryblock is impossible in themod_phpmodel. - Fatal errors (e.g.,
new ClassDoesntExist()) can’t be caught by anything. A lot of fairly innocuous things throw fatal errors, forcibly ending your program for questionable reasons. Shutdown functions still run, but they can’t get a stack trace (they run at top-level), and they can’t easily tell if the program exited due to an error or running to completion. - Trying to
throwan object that isn’t anExceptionresults in… a fatal error, not an exception.
- PHP errors (internal ones, and calls to
- There is no
finallyconstruct, making wrapper code (set handler, run code, unset handler; monkeypatch, run a test, unmonkeypatch) tedious and difficult to write. Despite that OO and exceptions were largely copied from Java, this is deliberate, becausefinally“doesn’t make much sense in the context of PHP”. Huh? (Fixed in 5.5.)
Functions
- Function calls are apparently rather expensive.
- Some built-in functions interact with reference-returning functions in, er, a strange way.
- As mentioned elsewhere, a lot of things that look like functions or look like they should be functions are actually language constructs, so nothing that works with functions will work with them.
- Function arguments can have “type hints”, which are basically just static typing. But you can’t require that an argument be an
intorstringorobjector other “core” type, even though every builtin function uses this kind of typing, probably becauseintis not a thing in PHP. (See above about(int).) You also can’t use the special pseudo-type decorations used heavily by builtin functions:mixed,number, orcallback. (callableis allowed as of PHP 5.4.)- As a result, this:
produces the error:function foo(string $s) {} foo("hello world");PHP Catchable fatal error: Argument 1 passed to foo() must be an instance of string, string given, called in... - You may notice that the “type hint” given doesn’t actually have to exist; there is no
stringclass in this program. If you try to useReflectionParameter::getClass()to examine the type hint dynamically, then it will balk that the class doesn’t exist, making it impossible to actually retrieve the class name. - A function’s return value can’t be hinted.
- As a result, this:
- Passing the current function’s arguments to another function (dispatch, not uncommon) is done by
call_user_func_array('other_function', func_get_args()). Butfunc_get_argsthrows a fatal error at runtime, complaining that it can’t be a function parameter. How and why is this even a type of error? (Fixed in PHP 5.3.) - Closures require explicitly naming every variable to be closed-over. Why can’t the interpreter figure this out? Kind of hamstrings the whole feature. (Okay, it’s because using a variable ever, at all, creates it unless explicitly told otherwise.)
- Closed-over variables are “passed” by the same semantics as other function arguments. That is, arrays and strings etc. will be “passed” to the closure by value. Unless you use
&. - Because closed-over variables are effectively automatically-passed arguments and there are no nested scopes, a closure can’t refer to private methods, even if it’s defined inside a class. (Possibly fixed in 5.4? Unclear.)
- No named arguments to functions. Actually explicitly rejected by the devs because it “makes for messier code”.
- Function arguments with defaults can appear before function arguments without, even though the documentation points out that this is both weird and useless. (So why allow it?)
- Extra arguments to a function are ignored (except with builtin functions, which raise an error). Missing arguments are assumed null.
- “Variadic” functions require faffing about with
func_num_args,func_get_arg, andfunc_get_args. There’s no syntax for such a thing.
OO
- The procedural parts of PHP are designed like C, but the objectional (ho ho) parts are designed like Java. I cannot overemphasize how jarring this is. The class system is designed around the lower-level Java language which is naturally and deliberately more limited than PHP’s contemporaries, and I am baffled.
- I’ve yet to find a global function that even has a capital letter in its name, yet important built-in classes use camelCase method names and have
getFooJava-style accessors. - Perl, Python, and Ruby all have some concept of “property” access via code; PHP has only the clunky
__getand friends. (The documentation inexplicably refers to such special methods as “overloading”.) - Classes have something like variable declaration (
varandconst) for class attributes, whereas the procedural part of the language does not. - Despite the heavy influence from C++/Java, where objects are fairly opaque, PHP often treats objects like fancy hashes—for example, the default behavior of
foreach ($obj as $key => $value)is to iterate over every accessible attribute of the object.
- I’ve yet to find a global function that even has a capital letter in its name, yet important built-in classes use camelCase method names and have
- Classes are not objects. Any metaprogramming has to refer to them by string name, just like functions.
- Built-in types are not objects and (unlike Perl) can in no way be made to look like objects.
instanceofis an operator, despite that classes were a late addition and most of the language is built on functions and function-ish syntax. Java influence? Classes not first-class? (I don’t know if they are.)- But there is an
is_afunction. With an optional argument specifying whether to allow the object to actually be a string naming a class. get_classis a function; there’s notypeofoperator. Likewiseis_subclass_of.- This doesn’t work on builtin types, though (again,
intis not a thing). For that, you needis_intetc. - Also the right-hand side has to be a variable or literal string; it can’t be an expression. That causes… a parse error.
- But there is an
cloneis an operator?!- Object attributes are
$obj->foo, but class attributes areClass::$foo. ($obj::$foowill try to stringify$objand use it as a class name.) Class attributes can’t be accessed via objects; the namespaces are completely separate, making class attributes completely useless for polymorphism. Class methods, of course, are exempt from this rule and can be called like any other method. (I am told C++ also does this. C++ is not a good example of fine OO.) - Also, an instance method can still be called statically (
Class::method()). If done so from another method, this is treated like a regular method call on the current$this. I think. new,private,public,protected,static, etc. Trying to win over Java developers? I’m aware this is more personal taste, but I don’t know why this stuff is necessary in a dynamic language—in C++ most of it’s about compilation and compile-time name resolution.- PHP has first-class support for “abstract classes”, which are classes that cannot be instantiated. Code in similar languages achieves this by throwing an exception in the constructor.
- Subclasses cannot override private methods. Subclass overrides of public methods can’t even see, let alone call, the superclass’s private methods. Problematic for, say, test mocks.
- Methods cannot be named e.g. “list”, because
list()is special syntax (not a function) and the parser gets confused. There’s no reason this should be ambiguous, and monkeypatching the class works fine. ($foo->list()is not a syntax error.) - If an exception is thrown while evaluating a constructor’s arguments (e.g.,
new Foo(bar())andbar()throws), the constructor won’t be called, but the destructor will be. (This is fixed in PHP 5.3.) - Exceptions in
__autoloadand destructors cause fatal errors. (Fixed in PHP 5.3.6. So now a destructor might throw an exception literally anywhere, since it’s called the moment the refcount drops the zero. Hmm.) - There are no constructors or destructors.
__constructis an initializer, like Python’s__init__. There is no method you can call on a class to allocate memory and create an object. - There is no default initializer. Calling
parent::__construct()if the superclass doesn’t define its own__constructis a fatal error. - OO brings with it an iterator interface that parts of the language (e.g.,
for...as) respect, but nothing built-in (like arrays) actually implements the interface. If you want an array iterator, you have to wrap it in anArrayIterator. There are no built-in ways to chain or slice or otherwise work with iterators as first-class objects. - Interfaces like
Iteratorreserve a good few unprefixed method names. If you want your class to be iterable (without the default behavior of iterating all of its attributes), but want to use a common method name likekeyornextorcurrent, well, too bad. - Classes can overload how they convert to strings and how they act when called, but not how they convert to numbers or any other builtin type.
- Strings, numbers, and arrays all have a string conversion; the language relies heavily on this. Functions and classes are
strings. Yet trying to convert a built-in or user-defined object (even
a Closure) to a string causes an error if it doesn’t define
__toString. Evenechobecomes potentially error-prone. - There is no overloading for equality or ordering.
- Static variables inside instance methods are global; they share the same value across all instances of the class.
Standard library
Perl is “some assembly required”. Python is “batteries included”. PHP is “kitchen sink, but it’s from Canada and both faucets are labeled C”.
General
- There is no module system. You can compile PHP extensions, but which ones are loaded is specified by php.ini, and your options are for an extension to exist (and inject its contents into your global namespace) or not.
- As namespaces are a recent feature, the standard library isn’t broken up at all. There are thousands of functions in the global namespace.
- Chunks of the library are wildly inconsistent from one another.
- Underscore versus not:
strpos/str_rot13,php_uname/phpversion,base64_encode/urlencode,gettype/get_class - “to” versus 2:
ascii2ebcdic,bin2hex,deg2rad,strtolower,strtotime - Object+verb versus verb+object:
base64_decode,str_shuffle,var_dumpversuscreate_function,recode_string - Argument order:
array_filter($input, $callback)versusarray_map($callback, $input),strpos($haystack, $needle)versusarray_search($needle, $haystack) - Prefix confusion:
usleepversusmicrotime - Case insensitive functions vary on where the
igoes in the name. - About half the array functions actually start with
array_. The others do not. htmlentitiesandhtml_entity_decodeare inverses of each other, with completely different naming conventions.
- Underscore versus not:
- Kitchen sink. The libary includes:
- Bindings to ImageMagick, bindings to GraphicsMagick (which is a fork of ImageMagick), and a handful of functions for inspecting EXIF data (which ImageMagick can already do).
- Functions for parsing bbcode, a very specific kind of markup used by a handful of particular forum packages.
- Way too many XML packages.
DOM(OO),DOM XML(not),libxml,SimpleXML, “XML Parser”,XMLReader/XMLWriter, and half a dozen more acronyms I can’t identify. There’s surely some kind of difference between these things and you are free to go figure out what that is. - Bindings for two particular credit card processors, SPPLUS and MCVE. What?
- Three ways to access a MySQL database:
mysql,mysqli, and thePDOabstraction thing.
C influence
This deserves its own bullet point, because it’s so absurd yet permeates the language. PHP is a high-level, dynamically-typed programming language. Yet a massive portion of the standard library is still very thin wrappers around C APIs, with the following results:
- “Out” parameters, even though PHP can return ad-hoc hashes or multiple arguments with little effort.
- At least a dozen functions for getting the last error from a particular subsystem (see below), even though PHP has had exceptions for eight years.
- Warts like
mysql_real_escape_string, even though it has the same arguments as the brokenmysql_escape_string, just because it’s part of the MySQL C API. - Global behavior for non-global functionality (like MySQL). Using multiple MySQL connections apparently requires passing a connection handle on every function call.
- The wrappers are really, really, really thin. For example, calling
dba_nextkeywithout callingdba_firstkeywill segfault. - The wrappers are often platform-specific:
fopen(directory, "r")works on Linux but returns false and generates a warning on Windows. - There’s a set of
ctype_*functions (e.g.ctype_alnum) that map to the C character-class detection functions of similar names, rather than, say,isupper.
Genericism
There is none. If a function might need to do two slightly different things, PHP just has two functions.
How do you sort backwards? In Perl, you might do sort { $b <=> $a }. In Python, you might do .sort(reverse=True). In PHP, there’s a separate function called rsort().
- Functions that look up a C error:
curl_error,json_last_error,openssl_error_string,imap_errors,mysql_error,xml_get_error_code,bzerror,date_get_last_errors, others? - Functions that sort:
array_multisort,arsort,asort,ksort,krsort,natsort,natcasesort,sort,rsort,uasort,uksort,usort - Functions that find text:
ereg,eregi,mb_ereg,mb_eregi,preg_match,strstr,strchr,stristr,strrchr,strpos,stripos,strrpos,strripos,mb_strpos,mb_strrpos, plus the variations that do replacements - There are a lot of aliases as well, which certainly doesn’t help matters:
strstr/strchr,is_int/is_integer/is_long,is_float/is_double,pos/current,sizeof/count,chop/rtrim,implode/join,die/exit,trigger_error/user_error,diskfreespace/disk_free_space… scandirreturns a list of files within a given directory. Rather than (potentially usefully) return them in directory order, the function returns the files already sorted. And there’s an optional argument to get them in reverse alphabetical order. There were not, apparently, enough sort functions. (PHP 5.4 adds a third value for the sort-direction argument that will disable sorting.)str_splitbreaks a string into chunks of equal length.chunk_splitbreaks a string into chunks of equal length, then joins them together with a delimiter.- Reading archives requires a separate set of functions depending on the format. There are six separate groups of such functions, all with different APIs, for bzip2, LZF, phar, rar, zip, and gzip/zlib.
- Because calling a function with an array as its arguments is so awkward (
call_user_func_array), there are some pairings likeprintf/vprintfandsprintf/vsprintf. These do the same things, but one function takes arguments and the other takes an array of arguments.
Text
preg_replacewith the/e(eval) flag will do a string replace of the matches into the replacement string, then eval it.strtokis apparently designed after the equivalent C function, which is already a bad idea for various reasons. Nevermind that PHP can easily return an array (whereas this is awkward in C), or that the very hackstrtok(3)uses (modifying the string in-place) isn’t used here.parse_strparses a query string, with no indication of this in the name. Also it acts just likeregister_globalsand dumps the query into your local scope as variables, unless you pass it an array to populate. (It returns nothing, of course.)exploderefuses to split with an empty/missing delimiter. Every other string split implementation anywhere does some useful default in this case; PHP instead has a totally separate function, confusingly calledstr_splitand described as “converting a string to an array”.- For formatting dates, there’s
strftime, which acts like the C API and respects locale. There’s alsodate, which has a completely different syntax and only works with English. - ”
gzgetss— Get line from gz-file pointer and strip HTML tags.” I’m dying to know the series of circumstances that led to this function’s conception. mbstring- It’s all about “multi-byte”, when the problem is character sets.
- Still operates on regular strings. Has a single global “default” character set. Some functions allow specifying charset, but then it applies to all arguments and the return value.
- Provides
ereg_*functions, but those are deprecated.preg_*are out of luck, though they can understand UTF-8 by feeding them some PCRE-specific flag.
System and reflection
- There are, in general, a whole lot of functions that blur the line between text and variables.
compactandextractare just the tip of the iceberg. - There are several ways to actually be dynamic in PHP, and at a glance there are no obvious differences or relative benefits.
classkitcan modify user-defined classes;runkitsupersedes it and can modify user-defined anything; theReflection*classes can reflect on most parts of the language; there are a great many individual functions for reporting properties of functions and classes. Are these subsystems independent, related, redundant? get_class($obj)returns the object’s class name.get_class()returns the name of the class the function is being called in. Setting aside that this one function does two radically different things:get_class(null)… acts like the latter. So you can’t trust it on an arbitrary value. Surprise!- The
stream_*classes allow for implementing custom stream objects for use withfopenand other fileish builtins. “tell” cannot be implemented for internal reasons. (Also there are A LOT of functions involved with this system.) register_tick_functionwill accept a closure object.unregister_tick_functionwill not; instead it throws an error complaining that the closure couldn’t be converted to a string.php_unametells you about the current OS. Unless PHP can’t tell what it’s running on; then it tells you about the OS it was built on. It doesn’t tell you if this has happened.forkandexecare not built in. They come with the pcntl extension, but that isn’t included by default.popendoesn’t provide a pid.stat’s return value is cached.session_decodeis for reading an arbitrary PHP session string, but it only works if there’s an active session already. And it dumps the result into$_SESSION, rather than returning it.
Miscellany
curl_multi_execdoesn’t changecurl_errnoon error, but it does changecurl_error.mktime’s arguments are, in order: hour, minute, second, month, day, year.
Data manipulation
Programs are nothing more than big machines that chew up data and spit out more data. A great many languages are designed around the kinds of data they manipulate, from awk to Prolog to C. If a language can’t handle data, it can’t do anything.
Numbers
- Integers are signed and 32-bit on 32-bit platforms. Unlike all of PHP’s contemporaries, there is no automatic bigint promotion. So you can end up with surprises like negative file sizes, and your math might work differently based on CPU architecture. Your only option for larger integers is to use the GMP or BC wrapper functions. (The developers have proposed adding a new, separate, 64-bit type. This is crazy.)
- PHP supports octal syntax with a leading
0, so e.g.012will be the number ten. However,08becomes the number zero. The8(or9) and any following digits disappear.01cis a syntax error. 0x0+2produces 4. The parser considers the2as both part of the hex literal and a separate decimal literal, treating this as0x002 + 2.0x0+0x2displays the same problem. Strangely,0x0 +2is still 4, but0x0+ 2is correctly 2. (This is fixed in PHP 5.4. But it’s also re-broken in PHP 5.4, with the new0bliteral prefix:0b0+1produces 2.)piis a function. Or there’s a constant,M_PI.- There is no exponentiation operator, only the
powfunction.
Text
- No Unicode support. Only ASCII will work reliably, really. There’s the
mbstringextension, mentioned above, but it kinda blows. - Which means that using the builtin string functions on UTF-8 text risks corrupting it.
- Similarly, there’s no concept of e.g. case comparisons outside of ASCII. Despite the proliferation of case-insensitive versions of functions, not one of them will consider
éequal toÉ. - You can’t quote keys in variable interpolation, i.e.,
"$foo['key']"is a syntax error. You can unquote it (which would generate a warning anywhere else!), or use${...}/{$...}. "${foo[0]}"is okay."${foo[0][0]}"is a syntax error. Putting the$on the inside is fine with both. Bad copy of similar Perl syntax (with radically different semantics)?
Arrays
Oh, man.
- This one datatype acts as a list, ordered hash, ordered set, sparse list, and occasionally some strange combination of those. How does it perform? What kind of memory use will there be? Who knows? Not like I have other options, anyway.
=>isn’t an operator. It’s a special construct that only exists insidearray(...)and theforeachconstruct.- Negative indexing doesn’t work, since
-1is just as valid a key as0. - Despite that this is the language’s only data structure, there is no shortcut syntax for it;
array(...)is shortcut syntax. (PHP 5.4 is bringing “literals”,[...].) - Similarly baffling, arrays stringify to
Arraywith an E_NOTICE. - The
=>construct is based on Perl, which allowsfoo => 1without quoting. (That is, in fact, why it exists in Perl; otherwise it’s just a comma.) In PHP, you can’t do this without getting a warning; it’s the only language in its niche that has no vetted way to create a hash without quoting string keys. -
Array functions often have confusing or inconsistent behavior because they have to operate on lists, hashes, or maybe a combination of the two. Consider
array_diff, which “computers the difference of arrays”.$first = array("foo" => 123, "bar" => 456); $second = array("foo" => 456, "bar" => 123); echo var_dump(array_diff($first, $second));What will this code do? If
array_difftreats its arguments as hashes, then obviously these are different; the same keys have different values. If it treats them as lists, then they’re still different; the values are in the wrong order.In fact
array_diffconsiders these equal, because it treats them like sets: it compares only values, and ignores order. - In a similar vein,
array_randhas the strange behavior of selecting random keys, which is not that helpful for the most common case of needing to pick from a list of choices. -
Despite how heavily PHP code relies on preserving key order:
array("foo", "bar") != array("bar", "foo") array("foo" => 1, "bar" => 2) == array("bar" => 2, "foo" => 1)I leave it to the reader to figure out what happens if the arrays are mixed. (I don’t know.)
array_fillcannot create zero-length arrays; instead it will issue a warning and return false.- All of the (many…) sort functions operate in-place and return nothing. There is no way to create a new sorted copy; you have to copy the array yourself, then sort it, then use the array.
- But
array_reversereturns a new array. - A list of ordered things and some mapping of keys to values sounds kind of like a great way to handle function arguments, but no.
Not arrays
- The standard library includes “Quickhash”, an OO implementation of “specific strongly-typed classes” for implementing hashes. And, indeed, there are four classes, each dealing with a different combination of key and value types. It’s unclear why the builtin array implementation can’t optimize for these extremely common cases, or what the relative performance is.
- There’s an
ArrayObjectclass (which implements five different interfaces) that can wrap an array and have it act like an object. User classes can implement the same interfaces. But it only has a handful of methods, half of which don’t resemble built-in array functions, and built-in array functions don’t know how to operate on anArrayObjector other array-like class.
Functions
- Functions are not data. Closures are actually objects, but regular functions are not. You can’t even refer to them with their bare names;
var_dump(strstr)issues a warning and assumes you mean the literal string,"strstr". There is no way to discern between an arbitrary string and a function “reference”. create_functionis basically a wrapper aroundeval. It creates a function with a regular name and installs it globally (so it will never be garbage collected—don’t use in a loop!). It doesn’t actually know anything about the current scope, so it’s not a closure. The name contains a NUL byte so it can never conflict with a regular function (because PHP’s parser fails if there’s aNULin a file anywhere).- Declaring a function named
__lambda_funcwill breakcreate_function—the actual implementation is toeval-create the function named__lambda_func, then internally rename it to the broken name. If__lambda_funcalready exists, the first part will throw a fatal error.
Other
- Incrementing (
++) aNULLproduces1. Decrementing (--) aNULLproducesNULL. Decrementing a string likewise leaves it unchanged. - There are no generators. (Fixed in 5.5. Wow. They basically cloned the entire Python generator API, too. Impressive. Somehow, though,
$foo = yield $bar;is a syntax error; it has to be$foo = (yield $bar). Sigh.)
Web framework
Execution
- A single shared file,
php.ini, controls massive parts of PHP’s functionality and introduces complex rules regarding what overrides what and when. PHP software that expects to be deployed on arbitrary machines has to override settings anyway to normalize its environment, which largely defeats the use of a mechanism likephp.inianyway.- PHP looks for
php.iniin a variety of places, so it may (or may not…) be possible to override your host’s. Only one such file will ever be parsed, though, so you can’t just override a couple settings and call it a day.
- PHP looks for
- PHP basically runs as CGI. Every time a page is hit, PHP recompiles the whole thing before executing it. Even dev servers for Python toy frameworks don’t act like this. This has led to a whole market of “PHP accelerators” that just compile once, accelerating PHP all the way to any other language. Zend, the company behind PHP, has made this part of their business model.
- For quite a long time, PHP errors went to the client by default—I guess to help during development. I don’t think this is true any more, but I still see the occasional mysql error spew at the top of a page.
- PHP is full of strange “easter eggs” like producing the PHP logo with the right query argument. Not only is this completely irrelevant to building your
application, but it allows detecting whether you’re using PHP (and perhaps roughly guessing what version), regardless of how much
mod_rewrite, FastCGI, reverse proxying, orServer:configuration you’re doing. - Blank lines before or after the
<?php ... ?>tags, even in libraries, count as literal text and is interpolated into the response (or causes “headers already sent” errors). Your options are to either strictly avoid extra blank lines at the end of every file (the one after the?>doesn’t count) or to just leave off the?>closing token.
Deployment
Deployment is often cited as the biggest advantage of PHP: drop some files and you’re done. Indeed, that’s much easier than running a whole process as you may have to do with Python or Ruby or Perl. But PHP leaves plenty to be desired.
Across the board, I’m in favor of running Web applications as app servers and reverse-proxying to them. It takes minimal effort to set this up, and the benefits are plenty: you can manage your web server and app separately, you can run as many or few app processes on as many machines as you want without needing more web servers, you can run the app as a different user with zero effort, you can switch web servers, you can take down the app without touching the web server, you can do seamless deployment by just switching where a fifo points, etc. Welding your application to your web server is absurd and there’s no good reason to do it any more.
- PHP is naturally tied to Apache. Running it separately, or with any other webserver, requires just as much mucking around (possibly more) as deploying any other language.
php.iniapplies to every PHP application run anywhere. There is only onephp.inifile, and it applies globally; if you’re on a shared server and need to change it, or if you run two applications that need different settings, you’re out of luck; you have to apply the union of all necessary settings and pare them down from inside the apps themselves usingini_setor in Apache’s configuration file or in.htaccess. If you can. Also wow that is a lot of places you need to check to figure out how a setting is getting its value.- Similarly, there is no easy way to “insulate” a PHP application and its dependencies from the rest of a system. Running two applications that require different versions of a library, or even PHP itself? Start by building a second copy of Apache.
- The “bunch of files” approach, besides making routing a huge pain in the ass, also means you have to carefully whitelist or blacklist what stuff is actually available, because your URL hierarchy is also your entire code tree. Configuration files and other “partials” need C-like guards to prevent them from being loaded directly. Version control noise (e.g.,
.svn) needs protecting. Withmod_php, everything on your filesystem is a potential entry point; with an app server, there’s only one entry point, and only the URL controls whether it’s invoked. - You can’t seamlessly upgrade a bunch of files that run CGI-style, unless you want crashes and undefined behavior as users hit your site halfway through the upgrade.
-
Despite how “simple” it is to configure Apache to run PHP, there are some subtle traps even there. While the PHP docs suggest using
SetHandlerto make.phpfiles run as PHP,AddHandlerappears to work just as well, and in fact Google gives me twice as many results for it. Here’s the problem.When you use
AddHandler, you are telling Apache that “execute this as php” is one possible way to handle.phpfiles. But! Apache doesn’t have the same idea of file extensions that every human being on the planet does. It’s designed to support, say,index.html.enbeing recognized as both English and HTML. To Apache, a file can have any number of file extensions simultaneously.Imagine you have a file upload form that dumps files into some public directory. To make sure nobody uploads PHP files, you just check that they don’t have a
.phpextension. All an attacker has to do is upload a file namedfoo.php.txt; your uploader won’t see a problem, but Apache will recognize it as PHP, and it will happily execute.The problem here isn’t “using the original filename” or “not validating better”; the problem is that your web server is configured to run any old code it runs across—precisely the same property that makes PHP “easy to deploy”. CGI required
+x, which was something, but PHP doesn’t even do that. And this is no theoretical problem; I’ve found multiple live sites with this issue.
Missing features
I consider all of these to be varying levels of critical for building a Web application. It seems reasonable that PHP, with its major selling point being that it’s a “Web language”, ought to have some of them.
- No template system. There’s PHP itself, but nothing that acts as a big interpolator rather than a program.
- No XSS filter. No, “remember to use
htmlspecialchars” is not an XSS filter. This is. - No CSRF protection. You get to do it yourself.
- No generic standard database API. Stuff like PDO has to wrap every individual database’s API to abstract the differences away.
- No routing. Your website looks exactly like your filesystem. Many developers have been tricked into thinking
mod_rewrite(and.htaccessin general) is an acceptable substitute. - No authentication or authorization.
- No dev server. (“Fixed” in 5.4. Led to the
Content-Lengthvuln below. Also, you have to port all your rewrite rules to a PHP wrapper thing, because there’s no routing.) - No interactive debugging.
- No coherent deployment mechanism; only “copy all these files to the server”.
Security
Language boundaries
PHP’s poor security reputation is largely because it will take arbitrary data from one language and dump it into another. This is a bad idea. "<script>" may not mean anything in SQL, but it sure does in HTML.
Making this worse is the common cry for “sanitizing your inputs”. That’s completely wrong; you can’t wave a magic wand to make a chunk of data inherently “clean”. What you need to do is speak the language: use placeholders with SQL, use argument lists when spawning processes, etc.
- PHP outright encourages “sanitizing”: there’s an entire data filtering extension for doing it.
- All the
addslashes,stripslashes, and other slashes-related nonsense are red herrings that don’t help anything. - There is, as far as I can tell, no way to safely spawn a process. You can ONLY execute a string via the shell. Your options are to escape like crazy and hope the default shell uses the right escaping, or
pcntl_forkandpcntl_execmanually. - Both
escapeshellcmdandescapeshellargexist with roughly similar descriptions. Note that on Windows,escapeshellargdoes not work (because it assumes Bourne shell semantics), andescapeshellcmdjust replaces a bunch of punctuation with spaces because nobody can figure out Windows cmd escaping (which may silently wreck whatever you’re trying to do). - The original built-in MySQL bindings, still widely-used, have no way to create prepared statements.
To this day, the PHP documentation on SQL injection recommends batty practices like type-checking, using sprintf and is_numeric, manually using mysql_real_escape_string everywhere, or manually using addslashes
everywhere (which “may be useful”!). There is no mention of PDO or paramaterization, except in the user comments. I complained about this very specifically to a PHP dev at least two years ago, he was alarmed, and the page has never changed.
Insecure-by-default
register_globals. It’s been off by default for a while by now, and it’s gone in 5.4. I don’t care. This is an embarrassment.includeaccepting HTTP URLs. Likewise.- Magic quotes. So close to secure-by-default, and yet so far from understanding the concept at all. And, likewise.
- You can, say, probe a network using PHP’s XML support, by abusing its ubiquitous support for filenames-as-URLs. Only
libxml_disable_entity_loader()can fix this, and the problem is only mentioned in the manual comments.
(5.5 brings a just-do-it password hashing function, password_hash, which should hopefully cut down on hand-rolled crypto code.)
Core
The PHP interpreter itself has had some fascinating security problems.
- In 2007 the interpreter had an integer overflow vulnerability. The fix started with
if (size > INT_MAX) return NULL;and went downhill from there. (For those not down with the C:INT_MAXis the biggest integer that will fit in a variable, ever. I hope you can figure out the rest from there.) - More recently, PHP 5.3.7 managed to include a
crypt()function that would, in effect, let anyone log in with any password. - PHP 5.4’s dev server is vulnerable to a denial of service, because it takes the
Content-Lengthheader (which anyone can set to anything) and tries to allocate that much memory. This is a bad idea.
I could dig up more but the point isn’t that there are X many exploits—software has bugs, it happens, whatever. The nature of these is horrifying. And I didn’t seek these out; they just happened to land on my doorstep in the last few months.
Conclusion
Some commentary has rightfully pointed out that I don’t have a conclusion. And, well, I don’t have a conclusion. If you got all the way down here, I assumed you agreed with me before you started ![]()
If you only know PHP and you’re curious to learn something else, give the Python tutorial a whirl and try Flask for the web stuff. (I’m not a huge fan of its template language, but it does the job.) It breaks apart the pieces of your app, but they’re still the same pieces and should look familiar enough. I might write a real post about this later; a whirlwind introduction to an entire language and web stack doesn’t belong down here.
Later or for bigger projects you may want Pyramid, which is medium-level, or Django, which is a complex monstrosity that works well for building sites like Django’s.
If you’re not a developer at all but still read this for some reason, I will not be happy until everyone on the planet has gone through Learn Python The Hard Way so go do that.
There’s also Ruby with Rails and some competitors I’ve never used, and Perl is still alive and kicking with Catalyst. Read things, learn things, build things, go nuts.
Credits
Thanks to the following for inspiration:
- PHP turtles
- PHP sadness
- PHP WTF
- YourLanguageSucks
- PHP in contrast to Perl
- Pi’s dense, angry, inspirational rant
- PHP is not an acceptable COBOL
- the PHP documentation
- a ton of PHP fanatics and PHP counter-fanatics
- and, of course, Rasmus Lerdorf for his wild misunderstanding of most of Perl
Let me know if you have any additions, or if I’m (factually!) wrong about something.
Debugging PHP applications with PhpStorm
Friday, February 21. 2014
Anybody who has reached a certain level of skill in software development eventually will start thinking about how to make the job easier or be more productive during the day. With computers and programming, the tools you're using is a good starting point.
I've written code with a number of text editors (including vim and notepad), some of them really bad and some of them more suited to the task at hand. IMHO one of the best editors for a software developer is Microsoft's Visual Studio. Since many of my projects involve PHP, that is not the optimal editor for that. For years I used Notepad++, but then I got a recommendation for JetBrains PhpStorm. Since that it has become my weapon of choice for PHP.
For example, debugging the application is very simple operation. PhpStorm has all the client-stuff built into it, the only thing that is needed is Xdebug-extension to the server end. In my case, my web server is on a Linux and I typically work on a Windows 7. The debugging is done over my LAN. There is a very good article on PhpStorm author's web site with name Zero-configuration Web Application Debugging with Xdebug and PhpStorm. I don't think the zero-configuration part is true, but it is almost zero anyway. ![]()
On the server end I have a PHP-fpm running, it has
php_admin_flag[xdebug.remote_enable] = on
php_admin_value[xdebug.remote_host] = my_machine_name
php_admin_value[xdebug.remote_port] = 9000
In the worker configuration. That enables the server side to initiate a DBGP-connection to the given client (PhpStorm) and start sending data there. There reference for all the configuration directives can be found from Xdebug's docs.
On the PhpStorm end all you have to do, is enable the listener:
Also I had to drill a hole into my Windows 7 firewall, to allow my web server to connect into TCP/9000. If you're running a single machine setup, that won't be necessary.
Any settings for the setup can be found in the PhpStorm project:
But I think they're ok as a default. At least I didn't change anything there. If your debugger does not work, you fumbled the settings or your listener is not enabled. On Windows, run this on command prompt to confirm:
PS J:\> netstat -ano
Active Connections
Proto Local Address Foreign Address State PID
TCP 0.0.0.0:9000 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING ?
It will return a long list of things, but one of the entries must be similar to that.
To make the choice between debugging and not debugging can be made really easy. There are a number of ways of starting a debug session, but for Firefox users there is an excellent add-on The easiest Xdebug. It will add an icon to your add-on bar:
If the bug is green, it will send a special cookie to the server during a page load request:
Cookie: XDEBUG_SESSION=netbeans-xdebug
That will initiate the debugging session for you and PhpStorm will stop on a breakpoint if one is set.
Switching to PhpStorm vastly improved my productivity. I would imagaine, that it will do that for anybody.
Zend Framework 2: Abusing ZeDb to manage multiple connections
Tuesday, February 18. 2014
My favorite way of approaching DAL in ZF2 is ZeDb. It uses lot of existing functionality, but adds a nice layer of its own stuff, and that stuff is really good. However, ZeDb has one single flaw, it does not support multiple database connections. The typical thinking is, that who an earth would want that. I do. I want other weird things too, but in an everyday real application, you simply need more connections than one.
I came up with an simple solution by abusing ZF2's ServiceManager. Typically you gain access to a model is via something like this:
$manager = $this->getServiceLocator()->get('ZeDbManager');
$model = $manager->get('Application\Entity\Prices');
To get that working you need to do the config in module.config.php, declare ZeDb's DatabaseManagerFactory and override Zend\Db\Adapter\Adapter with AdapterFactory and finally declare your DB-configuration and list the models. Its all in the ZeDb docs.
My idea exploits all three of those. I'll instantiate multiple DatabaseManagers via ServiceManager. Also, every model will select an existing DB-adapter for itself. To get that working there will be separate configuration for all of the connections.
Example module configuration:
return array(
'service_manager' => array(
'factories' => array(
'ZeDbManager' => 'ZeDb\Service\DatabaseManagerFactory',
'Zend\Db\Adapter\Adapter' => 'ZeDb\Service\AdapterFactory',
)
),
'zedb_db_in' => array(
'adapter' => array(
'driver' => 'pdo_pgsql',
),
'models' => array(
'Application\Model\Int\Products' => array(
'tableName' => 'products',
'entityClass' => 'Application\Entity\Int\Products',
),
),
),
'zedb_db_out' => array(
'adapter' => array(
'driver' => 'pdo_mysql',
),
'models' => array(
'Application\Model\Internal\Customers' => array(
'tableName' => 'customers',
'entityClass' => 'Application\Entity\Internal\Customers',
),
),
),
Here I declare the obligatory parts, and two separate configurations with names zedb_db_in and zedb_db_out.
I'll have to prime both the DatabaseManagers and Adapters in Module's onBootstrap(). After the objects exist, they are made accessible with:
public function getServiceConfig()
{
return array(
'factories' => array(
'zedb_db_in' => function (ServiceLocatorInterface $sm) {
return Module::getInDbManager();
},
'ZeDbAdapter_in' => function (ServiceLocatorInterface $sm) {
return Module::getInDbAdapter();
},
),
);
}
The model has to do some heavy lifting to get rid of the default Adapter:
class Products extends ZeDb\Model
{
public function __construct(Adapter $adapter, $options = null)
{
$adapter = $this->getDatabaseManager()
->getServiceLocator()
->get('ZeDbAdapter_in');
parent::__construct($adapter, $options);
}public function getDatabaseManager()
{
return Module::getInternalDbManager();
}
Now the setup is ready. In an action you can simply do:
$inDbManager = $this->getServiceLocator()->get('zedb_db_in');
$productsModel = $inDbManager->get('Application\Entity\Int\Products');
$products = $productsModel->SearchProductByCode('ABC123', null);
There is no limit on how many DB-connections you can have. Note that, the ZeDb-module bootstrap will initialize the default manager and adapter, but the idea is not to use them at all. Anyway, I'll stick with this until something better comes.
Zend Framework 2: Disable layout
Thursday, February 13. 2014
This topic pops up every once in a while. As default every rendered page implicitly renders a layout too. This is especially bad for JSON or XML or binary responses your application may generate as a response. So far the best explanation and some helpful insights is in Mr. Chris Schreiber's blog scribles.com in the article Disabling Layout in Zend Framework 2.
I was working on a web application, which was a machine-to-machine app and not meant for humans at all. So a layout is completely unnecessary. As Chris instructs, I went directly to the module-class and copy/pasted his code. It failed. He has some sort of typo in the code:
$sharedEventManager->attach(
'Zend\Mvc\Controller\AbstractController',
function(\Zend\Mvc\MvcEvent $event) {
When I was looking for SharedEventManagerInterface PHP-code, it says:
/**
* Attach a listener to an event
*
* @param string|array $id Identifier(s) for event emitting
* @param string $event
* @param callable $callback PHP Callback
* @param int $priority Priority at which listener should
* @return void
*/
public function attach($id, $event, $callback, $priority = 1);
There clearly are 3 obligatory parameters. Chris' code has three parameters with the optional priority. Something is missing. This is the fix:
$sharedEventManager->attach(
MvcEvent::EVENT_DISPATCH,
'Zend\Mvc\Controller\AbstractController',
function(\Zend\Mvc\MvcEvent $event) {
Now it works! However, as my application was in its early stages, I was missing the default controller with the class name of IndexController. Adding the code into onBootstrap() didn't help. None of the callback's code was run during event dispatch. More debugging revealed, that my code never triggered the MvcEvent::EVENT_DISPATCH. It did trigger a MvcEvent::EVENT_DISPATCH_ERROR instead. The reason is obvious, I didn't have the class.
For clarity I'll copy/paste my onBootstrap() entirely here:
public function onBootstrap(MvcEvent $evt)
{
$eventManager = $evt->getApplication()->getEventManager();
$sharedEventManager = $eventManager->getSharedManager();
// Make sure layout is not rendered for regular pages
$sharedEventManager->attach('Zend\Mvc\Controller\AbstractController',
MvcEvent::EVENT_DISPATCH,
function (MvcEvent $event) {
$dispatchResult = $event->getResult();
if ($dispatchResult instanceof ViewModel) {
$dispatchResult->setTerminal(true);
}
}, -99
);
// Make sure layout is not rendered for HTTP/404 pages
$eventManager->attach(MvcEvent::EVENT_DISPATCH_ERROR,
function (MvcEvent $event) {
$dispatchResult = $event->getResult();
if ($dispatchResult instanceof ViewModel) {
$dispatchResult->setTerminal(true);
}
}, -99
);
}
Now both events are handled properly, without attempting to find a layout. To test my code, I added a layout/layout.phtml to the project and commented out my above code. It did renader the file contents. Then I removed the comments and deleted the layout/-directory completely. My code still ran on both occasions: when action can be found and when action cannot be found. Actually I also have a CLI-interface to the app, but that won't render the layout anyway.
This is yet another example of the complexity of ZF2. Any trivial task turns out to be a huge pain in the butt. I don't want to start ranting about using PhpRenderer in CLI-app, that's a completely another complaint.
Managing PostgreSQL 8.x permissions to limit application user's access
Wednesday, February 5. 2014
I was working with a legacy project with PostgreSQL 8 installation. A typical software developer simply does not care about DBA enough to think more than once about the permissions setup. The thinking is that for the purpose of writing lines of working code which executes really nice SQL-queries a user with lots of power in its sleeves is a good thing. This is something I bump into a lot. It would be a nice eye-opener if every coder would had to investigate a server which has been cracked into once or twice in the early programming career. I'm sure that would improve the quality of code and improve security thinking.
Anyway, the logic for ignoring security is ok for a development box, given the scenario that it is pretty much inaccessible outside the development team. When going to production things always get more complicated. I have witnessed production boxes which are running applications that have been configured to access DB with Admin-permissions. That happens in an environment where any decent programmer/DBA can spot out a number of other ignored things. Thinking about security is both far above the pay-grade and the skill envelope your regular coder possesses.
In an attempt to do things the-right-way(tm), it is a really good idea to create a specific user for accessing the DB. Even better idea is to limit the permissions so, that application user cannot run the classic "; DROP TABLE users; -- " because lacking the permission to drop tables. We still remember Exploits of a Mom, right?
Image courtesy of xkcd.com.
Back to reality... I was on a production PostgreSQL and evaluated the situation. Database has owner of postgres, schema public had owner of postgres, but all the tables, sequences and views where owned by the application user. So any exploit would allow the application user to drop all tables. Not cool, huh! ![]()
To solve this three things are needed: first, owner of the entire schema must be postgres. Second, the application user needs only to have enough permission for CRUD-operations, nothing more. And third, the schema must not allow users to create new items on it. As default everybody can create new tables and sequences, but if somebody really pops your box and can run anything on your DB, creating new items (besides temporary tables) is not a good thing.
On a PostgreSQL 8 something of a trickery is needed. Version 9.0 introduced us the "GRANT ... ALL TABLES IN SCHEMA", but I didn't have that at my disposal. To get around the entire thing I created two SQL-queries which were crafted to output SQL-queries. I could simply copy/paste the output and run it in pgAdmin III query-window. Nice!
The first query to gather all tables and sequences and change the owner to postgres:
SELECT 'ALTER TABLE ' || table_schema || '.' || table_name ||' OWNER TO postgres;'
FROM information_schema.tables
WHERE
table_type = 'BASE TABLE' and
table_schema NOT IN ('pg_catalog', 'information_schema')
UNION
SELECT 'ALTER SEQUENCE ' || sequence_schema || '.' || sequence_name ||' OWNER TO postgres;'
FROM information_schema.sequences
WHERE
sequence_schema NOT IN ('pg_catalog', 'information_schema')
It will output something like this:
ALTER TABLE public.phones OWNER TO postgres;
ALTER SEQUENCE public.user_id_seq OWNER TO postgres;
I ran those, and owner was changed.
NOTE: that effectively locked the application user out of DB completely.
So it was time to restore access. This is the query to gather information about all tables, views, sequences and functions:
SELECT 'GRANT ALL ON ' || table_schema || '.' || table_name ||' TO my_group;'
FROM information_schema.tables
WHERE
table_type = 'BASE TABLE' and
table_schema NOT IN ('pg_catalog', 'information_schema')
UNION
SELECT 'GRANT ALL ON ' || table_schema || '.' || table_name ||' TO my_group;'
FROM information_schema.views
WHERE
table_schema NOT IN ('pg_catalog', 'information_schema')
UNION
SELECT 'GRANT ALL ON SEQUENCE ' || sequence_schema || '.' || sequence_name ||' TO my_group;'
FROM information_schema.sequences
WHERE
sequence_schema NOT IN ('pg_catalog', 'information_schema')
UNION
SELECT 'GRANT ALL ON FUNCTION ' || nspname || '.' || proname || '(' || pg_get_function_arguments(p.oid) || ') TO my_group;'
FROM pg_catalog.pg_proc p
INNER JOIN pg_catalog.pg_namespace n ON pronamespace = n.oid
WHERE
nspname = 'public'
It will output something like this:
GRANT ALL ON public.phones TO my_user;
GRANT ALL ON SEQUENCE public.user_id_seq TO my_user;
NOTE: you need to find/replace my_user to something that fits your needs.
Now the application was again running smoothly, but with reduced permission in effect. The problem with all this is that TRUNCATE-clause (or DELETE FROM -tablename-) are still working. To get the maximum out of enhanced security, some classification of data would be needed. But the client wasn't ready to do that (yet).
The third thing is to limit schema permissions so that only usage is allowed for the general public:
REVOKE ALL ON SCHEMA public FROM public;
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA public TO public;
Now only postgres can create new things there.
All there is to do at this point is to test the appliation. There should be errors for DB-access if something went wrong.
Zend Framework 2: Touching headLink() twice on layout template
Friday, January 17. 2014
This one was one of the tricky ones. My CSS-inclusion was doubled for a very strange reason. My layout-template has:
{$this->headLink()
->prependStylesheet('/css/style.css')
->prependStylesheet('/css/jQuery/jquery.mobile.css')}
{$this->headLink([
'rel' => 'shortcut icon',
'type' => 'image/vnd.microsoft.icon',
'href' => '/images/favicon.ico'
])}
That would be pretty standard for any web application. Link a couple of CSS-definition files and declare the URL for favorite icon of the website. However, on ZF2 doing things like my above code does, makes things go bad. Rather surprisingly, the HTML gets rendered as:
<link href="/css/jQuery/jquery.mobile.css" media="screen" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css">
<link href="/css/style.css" media="screen" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css">
<link href="/css/jQuery/jquery.mobile.css" media="screen" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css">
<link href="/css/style.css" media="screen" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css">
<link href="/images/favicon.ico" rel="shortcut icon" type="image/vnd.microsoft.icon">
It doesn't actually break anything to have the CSS linked twice, but it just makes the CSS-debugging bit weird. Lot of the declarations are twice in the list and browser has to determine which ones are effective and which ones are ignored in any particular case.
To find out what's going on, I swapped my template to contain:
{$this->headLink([
'rel' => 'shortcut icon',
'type' => 'image/vnd.microsoft.icon',
'href' => '/images/favicon.ico'
])}
{$this->headLink()
->prependStylesheet('/css/style.css')
->prependStylesheet('/css/jQuery/jquery.mobile.css')}
Whatta ... hell!? Now everything works as expected. First the favicon-link and then CSS-links. Without any unnecessary doubling.
After a nice long morning of debugging ZF2-view code revealed a solution:
{$this->headLink()
->prependStylesheet('/css/style.css')
->prependStylesheet('/css/jQuery/jquery.mobile.css')}
{$this->headLink()
->deleteContainer()}
{$this->headLink([
'rel' => 'shortcut icon',
'type' => 'image/vnd.microsoft.icon',
'href' => '/images/favicon.ico'
])}
Now everything renders nicely. No doubles, all in the order I wanted them to be. The key was to erase Zend\View\Helper\HeadLink's container after doing the stylesheets. The method is actually in the class Zend\View\Helper\Placeholder\Container\AbstractStandalone. Apparently headLink's container only adds up and any subsequent calls simply add to the existing storage. The mistake is to print the contents of the container in the middle. The final solution is not to touch headLink() twice:
{$this->headLink([
'rel' => 'shortcut icon',
'type' => 'image/vnd.microsoft.icon',
'href' => '/images/favicon.ico'
])
->prependStylesheet("/css/style.css")
->prependStylesheet("/css/jQuery/jquery.mobile.css")}
Now it works much better! The rendered HTML will have the items in appropriate order:
- /css/jQuery/jquery.mobile.css
- /css/style.css
- /images/favicon.ico
This was yet again one of the funny things that have changed since ZF1. I definitely would consider that as a bug, but don't want to bother sending Zend a report out of it. They'll yet again pull a Microsoft and declare it as a feature.
Zend Framework 2: preDispatch(), returning properly without executing action
Thursday, January 16. 2014
Getting ZF2 to do preDispatch() and postDispatch() like ZF1 had is widely known and documented. In your controller, add this:
protected function attachDefaultListeners()
{
parent::attachDefaultListeners();
$event_mgr = $this->getEventManager();
$event_mgr->attach('dispatch', array($this, 'preDispatch'), 100);
$event_mgr->attach('dispatch', array($this, 'postDispatch'), -100);
}
Two simple listeners are attached with proper priorities to trigger before and after the action.
However, to go somewhere else before the action is executed adds some complexity, as one can expect. In preDispatch() you can do one of two suggested things. A redirect:
// Do a HTTP/302 redirect
return $this->redirect()->toRoute(
'application', array('controller' => 'index', 'action' => 'index'
));
My issue here is, that it literally does a HTTP/302 redirect in your browser. Another problem is, that it still executes the action it was targeted to. It renders the view, runs all the listeners, does all the plugins and helpers as it started to do. It just redirects after all that. I don't want my user to do a redirect or to run all the bells and whistles including the action. Why cannot I simply return something else instead, like ZF1 could be programmed to do. On my top-1 list is to execute an action from another controller?
So, the another option to do is to simply call it quits right in the middle of preDispatch():
$url = $event->getRouter()
->assemble(
array('action' => 'index'),
array('name' => 'frontend')
);
$response = $event->getResponse();
$response->getHeaders()->addHeaderLine('Location', $url);
$response->setStatusCode(302);
$response->sendHeaders();
exit();
That's pretty much the same as previous, but uglier. exit()!! Really? In Zend Framework?! I'd rather keep the wheels rolling and machine turning like it normally would do until it has done all the dirty deeds it wants to do. Poking around The Net reveals, that nobody is really offering anything else. Apparently everybody simply are doing a copy/paste from the same sites I found.
This is what I offer. Discard the current operation, start a new one and return that! A lot better alternative.
Example 1, return JSON-data:
$event->stopPropagation(true);
// Skip executing the action requested. Return this instead.
$result = new JsonModel(array(
'success' => false,
'loginrequired' => true
));
$result->setTerminal(true);
$event->setResponse(new Response());
$event->setViewModel($result);
The key is in the setResponse()-call.
Example 2, call another action:
$event->stopPropagation(true);
// Skip executing the action requested.
// Execute anotherController::errorAction() instead.
$event->setResponse(new Response());
$result = $this->forward()->dispatch('Another', array(
'action' => 'error'
));
$result->setTerminal(true);
$event->setViewModel($result);
Hope this helps somebody else trying to do a ZF1 to ZF2 transition. In the end, there is only one thing similar between them. Their name has Zend Framwork in it. ![]()
git and HTTPS (fatal: HTTP request failed)
Friday, January 10. 2014
Two facts first about git:
- A number of sites tells you to use git:// or ssh:// instead of https://. Apparently there is some unnecessary complexity when piggy-backing over HTTP-secure.
- I personally don't like git due to it's complexity. Its like a requirement of being an experienced mechanic before getting a driver's license. You can drive a car without exact technical knowledge about the inner workings of a car. But that seems to be the only way to go with git.
So, I choose to run my own repo on my own box and do it over HTTPS. Since HTTPS is a 2nd class protocol in the git-world many simple things are unnecessarily difficult.
My initial attempt was to do a simple clone from my existing repo:
git clone https://me@my.server/my/Project
Well, that doesn't end well. There is this fully explanatory fatal: HTTP request failed -error. Adding --verbose does not help. Then I found a fact that git uses curl as it's HTTPS-transport client and very helpful environment variable to diagnose the problem:
export GIT_CURL_VERBOSE=1
git clone https://me@my.server/my/Project
That way I got the required debug-information about Certificate Authority -certificates being used. It didn't use my own CA's file at all.
The next fix was to tweak the configuration:
git config --global http.sslverify false
It made my clone working! That, however, is not the way I do computer security. I need my certificates verified. From git-config(1) man-page I found the required piece of information. Adding the CA-root path of my Linux-distro makes the entire thing working:
git config --global http.sslverify true
git config --global http.sslCAPath /etc/pki/tls/certs
Finally I found the good site about all this: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/3777075/ssl-certificate-rejected-trying-to-access-github-over-https-behind-firewall/4454754 It seems to contain all this information.
Unfortunately too late! But wouldn't it be great for git to emit the proper error message about the "Peer's certificate issuer is not recognized"? That was the original problem to begin with. Also, why don't CentOS-people configure their curl-library to behave like OpenSSL does?
Barcode weirdness: Exactly the same, but different
Tuesday, December 17. 2013
I was transferring an existing production web-application to a new server. There was a slight gap in the operating system version and I ended up refactoring lot of the code to compensate newer libraries in use. One of the issues I bumped into and spent a while fixing was barcode printing. It was a pretty standard Code 39 barcode for the shipping manifest.
The old code was using a commercial proprietary TrueType font file. I don't know when or where it was purchased by my client, but it was in production use in the old system. Looks like such a fonts sell for $99. Anyway, the new library had barcode printing in it, so I chose to use it.
Mistake. It does somewhat work. It prints a perfectly valid barcode. Example:
![]()
The issue is, that it does not read. I had a couple of readers to test with, and even the really expensive laser-one didn't register the code very well. So I had to re-write the printing code to simulate the old functionality. The idea is to read the TTF-font, convert it into some internal form and output a ready-to-go file into a data directory, so that conversion is needed only once. After that the library can read the font and produce nice looking graphics including barcodes. Here is an example of the TTF-style:
![]()
The difference is amazing! Any reader reads that easily. Both barcodes contain the same data in them, but they look so much different. Wow!
Perhaps one day a barcode wizard will explain me the difference between them.
Why cloud platforms exist - Benchmarking Windows Azure
Tuesday, October 8. 2013
I got permission to publish a grayed out version of a project I was contracted to do this summer. Since the customer paid big bucks for it, you're not going to see all the details. I'm sorry to act as a greedy idiot, but you have to hire me to do something similar to see your results.
The subject of my project is something that personally is intriguing to me: how much better does a cloud-native application perform when compared to a traditional LAMP-setup. I chose the cloud platform to be Windows Azure, since I know that one best.
The Setup
There was a pretty regular web-application for performing couple of specific tasks. Exactly the same sample data was populated to Azure SQL for IaaS-test and Azure Table Storage for PaaS -test. People who complain about using Azure SQL can imagine a faster setup being used on a virtual machine and expect the thing to perform faster.
To simulate a real web application, memory cache was used. Memcache for IaaS and Azure Cache for PaaS. On both occasions using memory cache pushes the performance of the application further as there is no need to do so much expensive I/O.
Results
In the Excel-charts there are number of simulated users at the horizontal axis. There are two vertical axis used for different items.
Following items can be read from the Excel-charts:
- Absolute number of pages served for giving measurement point (right axis)
- Absolute number of pages returned, which returned erroneous output (right axis)
- Percentage of HTTP-errors: a status code which we interpret as an error was returned (left axis)
- Percentage of total errors: HTTP errors + requests which did not return a status code (left axis)
- Number successful pages returned per second (left axis)
Results: IaaS
I took a ready-made CentOS Linux-image bundled with Nginx/PHP-FPM -pair and lured it to work under Azure and connect to ready populated data from Azure SQL. Here are the test runs from two and three medium instances.
Adding a machine to the service absolutely helps. With two instances, the application chokes completely at the end of test load. Added machine also makes the application perform much faster, there is a clear improvement on page load speed.
Results: PaaS
Exactly the same functionality was implemented with .Net / C#.
Here are the results:
Astonishing! Page load speed is so much higher on similar user loads, also no errors can be produced. I pushed the envelope with 40 times the users, but couldn't be sure if it was about test setup (which I definitely saturated) or Azure's capacity fluctuating under heavy load. The test with small role was also very satisfactory, it beats the crap out of running two medium instances on IaaS!
Conclusion
I have to state the obvious: PaaS-application performs much better. I just couldn't belive that it was impossible to get exact measurement from the point where the application chokes on PaaS.
Why Azure PaaS billing cannot be stopped? - revisit
Monday, October 7. 2013
In my earlier entry about Azure PaaS billing, I was complaining about how to stop the billing.
This time I managed to do it. The solution was simple: delete the deployments, but leave the cloud service intact. Then Azure stops reserving any (stopped) compute units for the cloud service. Like this:
Here is the proof:
Zero billing. Nice! ![]()
Why Azure PaaS billing cannot be stopped?
Tuesday, October 1. 2013
In Windows Azure stopping an IaaS virtual machine stops the billing, there is no need to delete the stopped instance. When you stop a PaaS cloud service, following happens:
Based on billing:
This is really true. On 26th and 27th I had a cloud service running on Azure, but I stopped it. On 28th and 29th there is billing for a service that has been stopped, and for which I got the warning about. I don't know why on 30th there is one core missing from the billing. Discount, perhaps? ![]()
My bottom line is:
Why? What possible idea could be, that your PaaS cloud service needs to be deleted in order to stop billing? Come on Microsoft! Equal rules for both cloud services!